Page 134 - Read Online
P. 134
new pockets for the correction of bottoming out, double does not allow areolar reduction that may overshadow
bubble deformity and animation deformities. [15-16] The use the true lift achieved in such cases presenting with
of these materials or techniques as supplementary breast large size NAC [Figure 3a and b]. In some cases, breast
supporting products are limited to reinforce or reconstruct envelope puckering along the lower edge of the upper
breast dimensions, to support weak breast envelope or split muscle can be obvious in the early period of
to prevent explant exposures but without the ability of healing but resolves in time [Figure 4]. The added use
reversing the NAC-inframammary crease (IMC) relationship of external supportive dressings stabilizes the mobilized
seen following breast ptosis and as defined by Regnault. skin envelope and conceals the temporary puckering
[9]
On the other hand, MIM has a unique ability to restore that can be worrying for the patients in the early stage
or improve the altered NAC-IMC relationship and without of healing. Removal of the dressings in 2 weeks’ time
extra scarring in selected cases. almost always leaves behind a smoother skin envelope
and muscle expansion and relaxation allows the implant
The augmentation mammoplasty with the internal
mastopexy in prepectoral or subglandular pocket to settle with more natural three-dimensional results
in revisionary cases has a marked advantage over [Figures 5 and 6].
simultaneous augmentation mammoplasty with the Even though the study did not include a very large number
internal mastopexy in primary cases. In primary cases, of patients, the outcome showed a very high satisfaction
especially those presenting with large size breasts, initial
acceptable results may later show sliding ptosis of the
NAC over the mound of the implant. However, when MIM
is performed in secondary cases, initial mammoplasty
in sub glandular pocket has generally compressed the
breast tissue over a period of time. This comparatively
thinner layer of the breast envelope is far easier to be
elevated, anchored, and secured at a higher position a
on the muscle, in a predictable way and with longevity
of results. The current series has a mean follow-up of
18 months (range: 6-48 months) with high satisfactory
results. Despite the much desired scar-less MIM in
selected cases, a longer follow-up will be desirable
for a comparison with other conventional mastopexy
techniques used today. The obvious disadvantage of
MIM is the indirect measurements for a nipple areolar b
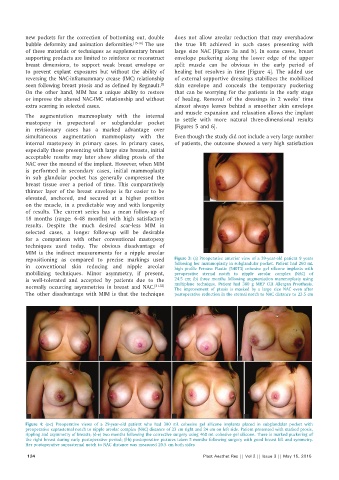
repositioning as compared to precise markings used Figure 3: (a) Preoperative anterior view of a 39-year-old patient 9 years
in conventional skin reducing and nipple areolar following her mammoplasty in subglandular pocket. Patient had 260 mL
high profile Perouse Plastie (540T3) cohesive gel silicone implants with
mobilizing techniques. Minor asymmetry, if present, preoperative sternal notch to nipple areolar complex (NAC) of
is well-tolerated and accepted by patients due to the 24.5 cm; (b) three months following augmentation mammoplasty using
normally occurring asymmetries in breast and NAC. [31-33] multiplane technique. Patient had 380 g MHP CUI Allergan Prosthesis.
The improvement of ptosis is masked by a large size NAC even after
The other disadvantage with MIM is that the technique postoperative reduction in the sternal notch to NAC distance to 23.5 cm
a b c d
e f g h
Figure 4: (a-c) Preoperative views of a 29-year-old patient who had 380 mL cohesive gel silicone implants placed in subglandular pocket with
preoperative suprasternal notch to nipple areolar complex (NAC) distance of 23 cm right and 24 cm on left side. Patient presented with marked ptosis,
rippling and asymmetry of breasts; (d-e) two months following the corrective surgery using 460 mL cohesive gel silicone. There is marked puckering of
the right breast during early postoperative period; (f-h) postoperative pictures taken 5 months following surgery with good breast lift and symmetry.
Her postoperative suprasternal notch to NAC distance was measured 20.5 cm both sides
124 Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 3 || May 15, 2015