Page 104 - Read Online
P. 104
The BFP was expanded and sutured with 4‑0 vicryl to DISCUSSION
the underlying wound. A saframycin based oral pack
was secured over the palate with 3‑0 vicryl suture for The use of BFP as a grafting source was first described
primary protection for 1 week till the epithelization in 1977 by Egyedi. Anatomically BFP is a fatty mass
[7]
begins, and strict soft diet was followed [Figure 5]. in the buccal space of the cheek. It comprises 3
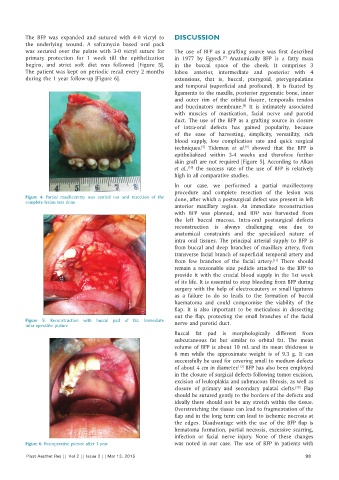
The patient was kept on periodic recall every 2 months lobes: anterior, intermediate and posterior with 4
during the 1 year follow‑up [Figure 6]. extensions, that is, buccal, pterygoid, pterygopalatine
and temporal (superficial and profound). It is fixated by
ligaments to the maxilla, posterior zygomatic bone, inner
and outer rim of the orbital fissure, temporalis tendon
and buccinators membrane. It is intimately associated
[8]
with muscles of mastication, facial nerve and parotid
duct. The use of the BFP as a grafting source in closure
of intra‑oral defects has gained popularity, because
of the ease of harvesting, simplicity, versatility, rich
blood supply, low complication rate and quick surgical
techniques. Tideman et al. showed that the BFP is
[9]
[5]
epithelialized within 3‑4 weeks and therefore further
skin graft are not required [Figure 5]. According to Alkan
et al., the success rate of the use of BFP is relatively
[10]
high in all comparative studies.
In our case, we performed a partial maxillectomy
procedure and complete resection of the lesion was
Figure 4: Partial maxillectomy was carried out and resection of the done, after which a postsurgical defect was present in left
complete lesion was done
anterior maxillary region. An immediate reconstruction
with BFP was planned, and BFP was harvested from
the left buccal mucosa. Intra‑oral postsurgical defects
reconstruction is always challenging one due to
anatomical constraints and the specialized nature of
intra oral tissues. The principal arterial supply to BFP is
from buccal and deep branches of maxillary artery, from
transverse facial branch of superficial temporal artery and
[11]
from few branches of the facial artery. There should
remain a reasonable size pedicle attached to the BFP to
provide it with the crucial blood supply in the 1st week
of its life. It is essential to stop bleeding from BFP during
surgery with the help of electrocautery or small ligatures
as a failure to do so leads to the formation of buccal
haematoma and could compromise the viability of the
flap. It is also important to be meticulous in dissecting
out the flap, protecting the small branches of the facial
Figure 5: Reconstruction with buccal pad of fat. Immediate nerve and parotid duct.
intra‑operative picture
Buccal fat pad is morphologically different from
subcutaneous fat but similar to orbital fat. The mean
volume of BFP is about 10 mL and its mean thickness is
6 mm while the approximate weight is of 9.3 g. It can
successfully be used for covering small to medium defects
[12]
of about 4 cm in diameter. BFP has also been employed
in the closure of surgical defects following tumor excision,
excision of leukoplakia and submucous fibrosis, as well as
[13]
closure of primary and secondary palatal clefts. Flap
should be sutured gently to the borders of the defects and
ideally there should not be any stretch within the tissue.
Overstretching the tissue can lead to fragmentation of the
flap and in the long term can lead to ischemic necrosis at
the edges. Disadvantage with the use of the BFP flap is
hematoma formation, partial necrosis, excessive scarring,
infection or facial nerve injury. None of these changes
Figure 6: Postoperative picture after 1 year was noted in our case. The use of BFP in patients with
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 2 || Mar 13, 2015 93