Page 58 - Read Online
P. 58
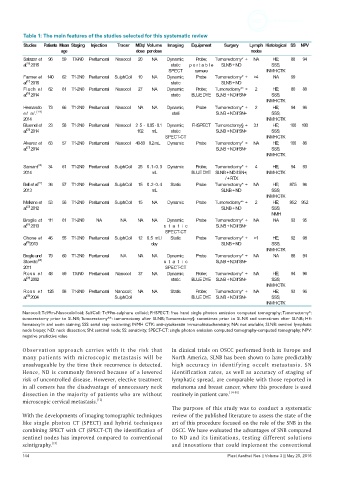
Table 1: The main features of the studies selected for this systematic review
Studies Patients Mean Staging Injection Tracer MBq/ Volume Imaging Equipment Surgery Lymph Histological SS NPV
age dose per dose nodes
Salazar et 96 59 TX-N0 Peritumoral Nanocoll 20 NA Dynamic; Probe; Tumorectomy* + NA HE; 88 94
[16]
al. 2015 static portable SLNB + ND SSS;
SPECT camera INMH CTK
Farmer et 140 62 T1-2N0 Peritumoral SulphColl 10 NA Dynamic; Probe Tumorectomy* + >4 NA 99
[17]
al. 2015 static SLNB + ND
Flach et 62 61 T1-2N0 Peritumoral Nanocoll 27 NA Dynamic; Probe; Tumorectomy** + 2 HE; 80 88
[18]
al. 2014 static BLUE DYE SLNB + ND if SN+ SSS;
INMH CTK
Hernando 73 66 T1-2N0 Peritumoral Nanocoll NA NA Dynamic; Probe Tumorectomy* + 2 HE; 94 96
et al. [19] stati SLNB + ND if SN+ SSS;
2014 INMH CTK
Bluemel et 23 58 T1-2N0 Peritumoral Nanocoll 25- 0.05 - 0.1 Dynamic; FHSPECT Tumorectomy§ + 3.1 HE; 100 100
al. 2014 102 mL static SLNB + ND if SN+ SSS;
[20]
SPECT-CT INMH CTK
Alvarez et 63 57 T1-2N0 Peritumoral Nanocoll 40-50 0.2 mL Dynamic Probe Tumorectomy* + NA HE; 100 86
[21]
al. 2014 SLNB + ND if SN+ SSS;
INMH CTK
[12]
Samant 34 61 T1-2N0 Peritumoral SulphColl 25 0.1-0.3 Dynamic Probe; Tumorectomy* + 4 HE; 94 93
2014 mL BLUE DYE SLNB + ND if SN+; INMH CTK
/ + RTX
[22]
Bell et al. 36 57 T1-2N0 Peritumoral SulphColl 15 0.2-0.4 Static Probe Tumorectomy* + NA HE; 87.5 96
2013 mL SLNB + ND SSS;
INMH CTK
Melkane et 53 56 T1-2N0 Peritumoral SulphColl 15 NA Dynamic Probe Tumorectomy** + 2 HE; 95.2 95.2
[23]
al. 2012 SLNB + ND SSS;
INMH
Broglie et 111 61 T1-2N0 NA NA NA NA Dynamic; Probe Tumorectomy* + NA NA 93 95
[24]
al. 2013 s t at ic SLNB + ND if SN+
SPECT-CT
Chone et 46 55 T1-2N0 Peritumoral SulphColl 12 0.5 mL/ Static Probe Tumorectomy* + >1 HE; 92 98
[25]
al. 2013 day SLNB + ND SSS;
INMH CTK
Broglie and 79 60 T1-2N0 Peritumoral NA NA NA Dynamic; Probe Tumorectomy* + NA NA 88 94
[26]
Stoeckli s t at ic SLNB + ND if SN+
2011 SPECT-CT
Ross et 48 59 TX-N0 Peritumoral Nanocoll 37 NA Dynamic; Probe; Tumorectomy* + NA HE; 94 96
al. 2002 static BLUE DYE SLNB + ND if SN+ SSS;
[29]
INMH CTK
Ross et 125 58 T1-2N0 Peritumoral Nanocoll; NA NA Static Probe; Tumorectomy* + NA HE; 93 96
[30]
al. 2004 SulphColl BLUE DYE SLNB + ND if SN+ SSS;
INMH CTK
Nanocoll: Tc99m-Nanocololloid; SulfColl: Tc99m-sulphure colloid; FHSPECT: free hand single photon emission computed tomography; Tumorectomy*:
tumorectomy prior to SLNB; Tumorectomy**: tumorectomy after SLNB; Tumorectomy§: sometimes prior to SLNB and sometimes after SLNB; HE:
hematoxylin and eosin staining; SSS: serial step sectioning; INMH CTK: anti-cytokeratin immunohistochemistry; NA: not available; SLNB: sentinel lymphatic
node biopsy; ND: neck dissection; SN: sentinel node; SS: sensitivity; SPECT-CT: single photon emission computed tomography-computed tomography; NPV:
negative predictive value
Observation approach carries with it the risk that In clinical trials on OSCC performed both in Europe and
many patients with microscopic metastasis will be North America, SLNB has been shown to have predictably
unsalvageable by the time their recurrence is detected. high accuracy in identifying occult metastasis. SN
Hence, ND is commonly favored because of a lowered identification rates, as well as accuracy of staging of
risk of uncontrolled disease. However, elective treatment lymphatic spread, are comparable with those reported in
in all comers has the disadvantage of unnecessary neck melanoma and breast cancer, where this procedure is used
dissection in the majority of patients who are without routinely in patient care. [14-16]
microscopic cervical metastasis. [12]
The purpose of this study was to conduct a systematic
With the developments of imaging tomographic techniques review of the published literature to assess the state of the
like single photon CT (SPECT) and hybrid techniques art of this procedure focused on the role of the SNB in the
combining SPECT with CT (SPECT-CT) the identification of OSCC. We have evaluated the advantages of SNB compared
sentinel nodes has improved compared to conventional to ND and its limitations, testing different solutions
[13]
scintigraphy. and innovations that could implement the conventional
144 Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || May 25, 2016