Page 26 - Read Online
P. 26
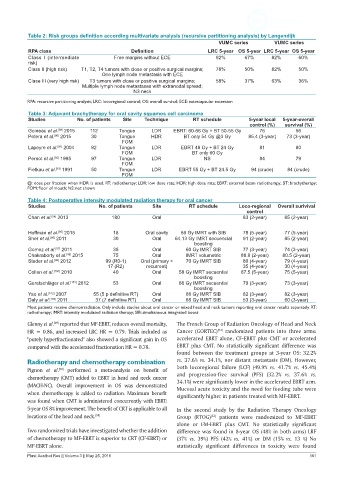
Table 2: Risk groups definition according multivariate analysis (recursive partitioning analysis) by Langendijk
VUMC series VUMC series
RPA class Definition LRC 5-year OS 5-year LRC 5-year OS 5-year
Class I (intermediate Free margins without ECE 92% 67% 82% 60%
risk)
Class II (high risk) T1, T2, T4 tumors with close or positive surgical margins; 78% 50% 82% 50%
One lymph node metastasis with ECE
Clase III (very high risk) T3 tumors with close or positive surgical margins; 58% 37% 63% 36%
Multiple lymph node metastases with extranodal spread;
N3 neck
RPA: recursive partitioning analysis; LRC: locoregional control; OS: overall survival; ECE: extracapsular extension
Table 3: Adjuvant brachytherapy for oral cavity squamos cell carcinoma
Studies No. of patients Site Technique RT schedule 5-year local 5-year-overall
control (%) survival (%)
Goineau et al. 2015 112 Tongue LDR EBRT: 60-66 Gy + BT 50-55 Gy 76 56
[89]
Petera et al. 2015 30 Tongue HDR BT only 54 Gy @3 Gy 85.4 (3-year) 73 (3-year)
[90]
FOM
Lapeyre et al. 2004 82 Tongue LDR EBRT 48 Gy + BT 24 Gy 81 80
[91]
FOM BT only 60 Gy
Pernot et al. 1995 97 Tongue LDR NS 84 79
[92]
FOM
Fietkau et al. 1991 50 Tongue LDR EBRT 55 Gy + BT 24.5 Gy 94 (crude) 84 (crude)
[93]
FOM
@: dose per fraction when HDR is used. RT: radiotherapy; LDR: low dose rate; HDR: high dose rate; EBRT: external beam radiotherapy; BT: brachytherapy;
FOM: floor of mouth; NS: not shown
Table 4: Postoperative intensity modulated radiation therapy for oral cancer
Studies No. of patients Site RT schedule Loco-regional Overall surivival
control
Chan et al. 2013 180 Oral 83 (2-year) 65 (2-year)
[94]
Hoffman et al. 2015 18 Oral cavity 66 Gy IMRT with SIB 78 (5-year) 77 (5-year)
[95]
Sher et al. 2011 30 Oral 64.13 Gy IMRT secuencial 91 (2-year) 85 (2-year)
[96]
boosting
[97]
Gomez et al. 2011 35 Oral 60 Gy IMRT SIB 77 (3-year) 74 (3-year)
Chakraborty et al. 2015 75 Oral IMRT volumetric 88.9 (2-year) 80.5 (2-year)
[98]
Studer et al. 2012 99 (R0-1) Oral (primary + 70 Gy IMRT SIB 80 (4-year) 79 (4-year)
[99]
17 (R2) recurrent) 35 (4-year) 30 (4-year)
Collan et al. [100] 2010 40 Oral 58 Gy IMRT secuential 87.5 (5-year) 75 (5-year)
boosting
Geretschläger et al. [101] 2012 53 Oral 66 Gy IMRT secuential 79 (3-year) 73 (3-year)
boosting
Yao et al. [102] 2007 55 (5 p definitive RT) Oral 66 Gy IMRT SIB 82 (3-year) 82 (3-year)
Daly et al. [103] 2011 37 (7 definitive RT) Oral 66 Gy IMRT SIB 53 (3-year) 60 (3-year)
Most patients receive chemoirradiation. Only include studies about oral cancer or mixed head and neck tumors reporting oral cancer results separately. RT:
radiotherapy; IMRT: intensity modulated radiation therapy; SIB: simultaneous integrated boost
[49]
Glenny et al. reported that MF-EBRT, reduces overall mortality, The French Group of Radiation Oncology of Head and Neck
HR = 0.86, and increased LRC HR = 0.79. Trials included as Cancer (GORTEC) randomized patients into three arms:
[52]
"purely hyperfractionated" also showed a significant gain in OS accelerated EBRT alone, CF-EBRT plus CMT or accelerated
compared with the accelerated fractionation HR = 0.78. EBRT plus CMT. No statistically significant difference was
found between the treatment groups at 3-year OS: 32.2%
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy combination vs. 37.6% vs. 34.1%, nor distant metastasis (DM). However,
[50]
Pignon et al. performed a meta-analysis on benefit of both locoregional failure (LCF) (49.9% vs. 41.7% vs. 45.4%)
chemotherapy (CMT) added to EBRT in head and neck cancer and progression-free survival (PFS) (32.2% vs. 37.6% vs.
(MACH-NC). Overall improvement in OS was demonstrated 34.1%) were significantly lower in the accelerated EBRT arm.
Mucosal acute toxicity and the need for feeding tube were
when chemotherapy is added to radiation. Maximum benefit significantly higher in patients treated with MF-EBRT.
was found when CMT is administered concurrently with EBRT:
5-year OS 8% improvement. The benefit of CRT is applicable to all In the second study by the Radiation Therapy Oncology
locations of the head and neck. [51] Group (RTOG) patients were randomized to MF-EBRT
[53]
alone or FM-EBRT plus CMT. No statistically significant
Two randomized trials have investigated whether the addition difference was found in 8-year OS (48% in both arms) LRF
of chemotherapy to MF-EBRT is superior to CRT (CF-EBRT) or (37% vs. 39%) PFS (42% vs. 41%) or DM (15% vs. 13 %) No
MF-EBRT alone. statistically significant differences in toxicity were found
Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || May 25, 2016 161