Page 17 - Read Online
P. 17
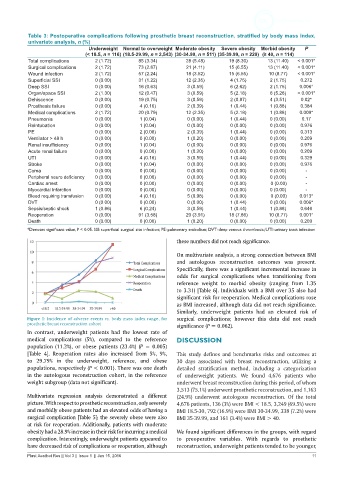
Table 3: Postoperative complications following prosthetic breast reconstruction, stratified by body mass index,
univariate analysis, n (%)
Underweight Normal to overweight Moderate obesity Severe obesity Morbid obesity P
(< 18.5, n = 116) (18.5-29.99, n = 2,543) (30-34.99, n = 511) (35-39.99, n = 229) (≥ 40, n = 114)
Total complications 2 (1.72) 85 (3.34) 28 (5.48) 19 (8.30) 13 (11.40) < 0.001*
Surgical complications 2 (1.72) 73 (2.87) 21 (4.11) 15 (6.55) 13 (11.40) < 0.001*
Wound infection 2 (1.72) 57 (2.24) 18 (3.52) 15 (6.55) 10 (8.77) < 0.001*
Superficial SSI 0 (0.00) 31 (1.22) 12 (2.35) 4 (1.75) 2 (1.75) 0.272
Deep SSI 0 (0.00) 16 (0.63) 3 (0.59) 6 (2.62) 2 (1.75) 0.006*
Organ/space SSI 2 (1.30) 12 (0.47) 3 (0.59) 5 (2.18) 6 (5.26) < 0.001*
Dehiscence 0 (0.00) 19 (0.75) 3 (0.59) 2 (0.87) 4 (3.51) 0.02*
Prosthesis failure 0 (0.00) 4 (0.16) 2 (0.39) 1 (0.44) 1 (0.88) 0.384
Medical complications 2 (1.72) 20 (0.79) 12 (2.35) 5 (2.18) 1 (0.88) 0.009*
Pneumonia 0 (0.00) 1 (0.04) 0 (0.00) 1 (0.44) 0 (0.00) 0.17
Reintubation 0 (0.00) 1 (0.04) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0.976
PE 0 (0.00) 2 (0.08) 2 (0.39) 1 (0.44) 0 (0.00) 0.313
Ventilator > 48 h 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 1 (0.20) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0.209
Renal insufficiency 0 (0.00) 1 (0.04) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0.976
Acute renal failure 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 1 (0.20) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0.209
UTI 0 (0.00) 4 (0.16) 3 (0.59) 1 (0.44) 0 (0.00) 0.329
Stroke 0 (0.00) 1 (0.04) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0.976
Coma 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) ‑
Peripheral neuro deficiency 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) ‑
Cardiac arrest 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) ‑
Myocardial Infarction 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) ‑
Bleed requiring transfusion 0 (0.00) 4 (0.16) 5 (0.98) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0.013*
DVT 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 1 (0.44) 0 (0.00) 0.006*
Sepsis/septic shock 1 (0.86) 6 (0.24) 3 (0.59) 1 (0.44) 1 (0.88) 0.646
Reoperation 0 (0.00) 91 (3.58) 20 (3.91) 18 (7.86) 10 (8.77) 0.001*
Death 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 1 (0.20) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 0.209
*Denotes significant value, P < 0.05. SSI: superficial surgical site infection; PE: pulmonary embolism; DVT: deep venous thrombosis; UTI: urinary tract infection
these numbers did not reach significance.
On multivariate analysis, a strong connection between BMI
and autologous reconstruction outcomes was present.
Specifically, there was a significant incremental increase in
odds for surgical complications when transitioning from
reference weight to morbid obesity (ranging from 1.35
to 3.31) [Table 6]. Individuals with a BMI over 35 also had
significant risk for reoperation. Medical complications rose
as BMI increased, although data did not reach significance.
Similarly, underweight patients had an elevated risk of
Figure 1: Incidence of adverse events vs. body mass index range, for surgical complications; however this data did not reach
prosthetic breast reconstruction cohort significance (P = 0.062).
In contrast, underweight patients had the lowest rate of
medical complications (5%), compared to the reference DISCUSSION
population (11.2%), or obese patients (23.4%) (P = 0.005)
[Table 4]. Reoperation rates also increased from 5%, 9%, This study defines and benchmarks risks and outcomes at
to 29.79% in the underweight, reference, and obese 30 days associated with breast reconstruction, utilizing a
populations, respectively (P < 0.001). There was one death detailed stratification method, including a categorization
in the autologous reconstruction cohort, in the reference of underweight patients. We found 4,676 patients who
weight subgroup (data not significant). underwent breast reconstruction during this period, of whom
3,513 (75.1%) underwent prosthetic reconstruction, and 1,163
Multivariate regression analysis demonstrated a different (24.9%) underwent autologous reconstruction. Of the total
picture. With respect to prosthetic reconstruction, only severely 4,676 patients, 136 (3%) were BMI < 18.5, 3,249 (69.5%) were
and morbidly obese patients had an elevated odds of having a BMI 18.5-30, 792 (16.9%) were BMI 30-34.99, 338 (7.2%) were
surgical complication [Table 5]; the severely obese were also BMI 35-39.99, and 161 (3.4%) were BMI > 40.
at risk for reoperation. Additionally, patients with moderate
obesity had a 28.9% increase in their risk for incurring a medical We found significant differences in the groups, with regard
complication. Interestingly, underweight patients appeared to to preoperative variables. With regards to prosthetic
have decreased risk of complications or reoperation, although reconstruction, underweight patients tended to be younger,
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 3 || Issue 1 || Jan 15, 2016 11