Page 24 - Read Online
P. 24
If the traumas are not diagnosed or well treated in a timely mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and the contour or
[8]
fashion, patients can suffer from functional and aesthetic form factor needs special attention. A recent article argues
sequelae. that the ideal implant should be discussed in seven points:
(1) stability and fixation; (2) contouring and handling; (3)
In 1889, Lang was first to recognize that traumatic biological behavior; (4) drainage; (5) donor site morbidity;
[3]
enophthalmos is caused by fracture of the orbital wall and the (6) radiopacity; and (7) availablility and cost-effectiveness. [5]
associated orbital tissue abnormality. Significant progress
has been made in the field of orbital reconstruction. It’s First of all, the ideal material is expected to be strong enough
commonly believed that orbital deformities occur because to support the orbital content, to be stable, to maintain its
of two main causes: first, the anatomic changes behind the shape over time, and to fix itself to surrounding structures.
eyeball that may consist of an inferior dislocation of the Second, it should be malleabile with a smooth surface. A
orbital floor or a transversal expansion of the orbit which desirable implant needs to be of high biocompatibility,
[4]
contributes to the defect; second, once soft tissue within chemically inert, non-allergenic and non-carcinogenic to
the socket is affected, the whole socket can be influenced. ensure a decrease in rates of infection/extrusion/migration/
Thus, we are supposed not only to repair the orbital fracture, foreign body reaction. It must allow high tissue incorporation
but also find the appropriate filling materials to restore the with minimal resorption. Furthermore, spaces within the
volume of orbit, avoiding bothersome sequelae, and restore implant should be present to allow drainage of orbital
ocular functions. fluid. Materials that are radiopaque facilitate postoperative
evaluation. Lastly, it should be readily available, in sufficient
Orbital fractures occur with bothersome complications like quantities, and have an acceptable cost to ensure easy
enophthalmos and constant diplopia. Among 55 studies popularization.
performed on orbital reconstruction, it was found that the
indication for surgery was based on diplopia in 18.3% of BIOMATERIALS
cases and on preoperative enophthalmos in 29.8% of cases.
[5]
The goal of orbital reconstruction is to repair trauma defects, Biological materials including autografts, allografts, and
to correct the anatomical position of the eye, to accurately xenografts, are defined as grafts harvested from the same
restore the volume of the orbit, to avoid sequelae such body, from cadavers or from animals. Generally speaking,
as enophthalmos, and to restore ocular function. Orbital autologous grafts are characterized by cost-effectiveness
fractures can occur alone or with other craniomaxillofacial but limited availability, variable resorption rates resulting in
fractures, which may complicate the reconstruction. It’s unpredictable orbital volume that may lead to enophthalmos,
reported that the medial wall and the orbital floor fractures associated donor site morbidity (pain, scarring, infection,
are the most frequent type. The medial wall of the orbit haematoma), as well as an increased surgical time. Autologous
consists of the maxilla, lacrimal, ethmoid and sphenoid bone was the first material used to reconstruct the orbit and
bones, and it is the most vulnerable and most complicated remains popular today. Since the 18th century, it has been
to repair due to its anatomical structure. Small defects may the “gold standard” biomaterial for the reconstruction of
heal alone by the formation of scar tissue, whereas larger craniofacial bony defects. [9,10] The major donor sites include
defects, especially those associated with enophthalmos and crista iliaca, calvarium, maxilla and mandible. [11-14] Autologous
hypoglobus, need material of a sufficient strength to support bone graft is applied in orbital reconstruction because of its
the orbital contents and restore the contour of the orbit. [6] strength, rigidity, biocompatibility, vascularization potential,
and incorporation into the orbital tissue with minimal acute
In terms of operation, we should consider three pivotal and chronic immune reactivity. The advantages mentioned
questions. When is the best timing to perform the operation? above make it a significant role in the stage of orbital
How to perform the operation? What materials should be
used? This review aims to give a comprehensive overview
of the advantages and disadvantages of materials used to
repair orbital fractures or used for soft tissue defect filling,
with the goal of assisting surgeons to make a better choice.
THE IDEAL IMPLANT MATERIAL
FOR ORBITAL FRACTURE
RECONSTRUCTION
It’s very difficult to determine which material is the ideal
implant for orbital fracture reconstruction. The ideal
characteristics of the material used as an orbital implant
include: (1) ability to bend into an anatomical shape; (2)
radiopacity; and (3) permanent stability. For smaller
[5]
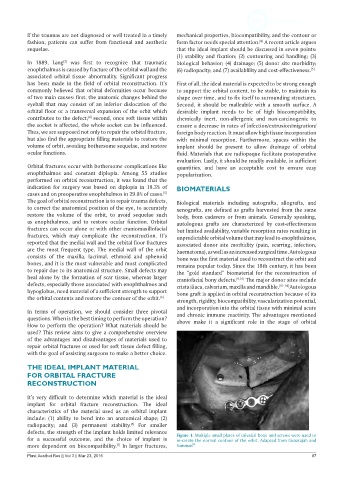
defects, the strength of the implant holds limited relevance Figure 1: Multiple small plates of calvarial bone and screws were used to
for a successful outcome, and the choice of implant is re-create the normal contour of the orbit. Adapted from Gunarajah and
[7]
more dependent on biocompatibility. In larger fractures, Samman [6]
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 3 || Mar 23, 2016 87