Page 37 - Read Online
P. 37
Bizic et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2022;9:14 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2021.102 Page 9 of 12
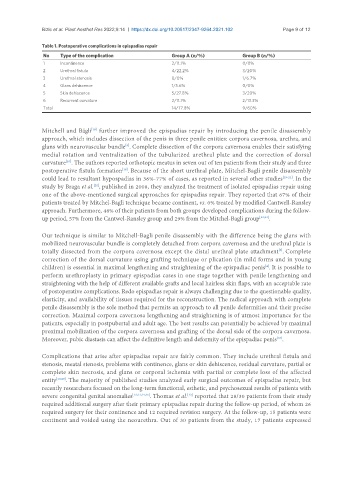
Table 1. Postoperative complications in epispadias repair
No Type of the complication Group A (n/%) Group B (n/%)
1 Incontinence 2/11.1% 0/0%
2 Urethral fistula 4/22.2% 3/20%
3 Urethral stenosis 0/0% 1/6.7%
4 Glans dehiscence 1/5.6% 0/0%
5 Skin dehiscence 5/27.8% 3/20%
6 Recurrent curvature 2/11.1% 2/13.3%
Total 14/77.8% 9/60%
Mitchell and Bägli further improved the epispadias repair by introducing the penile disassembly
[18]
approach, which includes dissection of the penis in three penile entities: corpora cavernosa, urethra, and
glans with neurovascular bundle . Complete dissection of the corpora cavernosa enables their satisfying
[9]
medial rotation and ventralization of the tubularized urethral plate and the correction of dorsal
curvature . The authors reported orthotopic meatus in seven out of ten patients from their study and three
[10]
postoperative fistula formation . Because of the short urethral plate, Mitchel-Bagli penile disassembly
[18]
could lead to resultant hypospadias in 36%-77% of cases, as reported in several other studies [19-21] . In the
study by Braga et al. , published in 2008, they analyzed the treatment of isolated epispadias repair using
[22]
one of the above-mentioned surgical approaches for epispadias repair. They reported that 67% of their
patients treated by Mitchel-Bagli technique became continent, vs. 0% treated by modified Cantwell-Ransley
approach. Furthermore, 48% of their patients from both groups developed complications during the follow-
up period, 57% from the Cantwel-Ransley group and 29% from the Mitchel-Bagli group [22,23] .
Our technique is similar to Mitchell-Bagli penile disassembly with the difference being the glans with
mobilized neurovascular bundle is completely detached from corpora cavernosa and the urethral plate is
totally dissected from the corpora cavernosa except the distal urethral plate attachment . Complete
[5]
correction of the dorsal curvature using grafting technique or plication (in mild forms and in young
children) is essential in maximal lengthening and straightening of the epispadiac penis . It is possible to
[4]
perform urethroplasty in primary epispadias cases in one stage together with penile lengthening and
straightening with the help of different available grafts and local hairless skin flaps, with an acceptable rate
of postoperative complications. Redo epispadias repair is always challenging due to the questionable quality,
elasticity, and availability of tissues required for the reconstruction. The radical approach with complete
penile disassembly is the sole method that permits an approach to all penile deformities and their precise
correction. Maximal corpora cavernosa lengthening and straightening is of utmost importance for the
patients, especially in postpubertal and adult age. The best results can potentially be achieved by maximal
proximal mobilization of the corpora cavernosa and grafting of the dorsal side of the corpora cavernosa.
Moreover, pubic diastasis can affect the definitive length and deformity of the epispadiac penis .
[10]
Complications that arise after epispadias repair are fairly common. They include urethral fistula and
stenosis, meatal stenosis, problems with continence, glans or skin dehiscence, residual curvature, partial or
complete skin necrosis, and glans or corporal ischemia with partial or complete loss of the affected
entity [10,20] . The majority of published studies analyzed early surgical outcomes of epispadias repair, but
recently researchers focused on the long-term functional, esthetic, and psychosexual results of patients with
[13]
severe congenital genital anomalies [13,21,24,25] . Thomas et al. reported that 28/30 patients from their study
required additional surgery after their primary epispadias repair during the follow-up period, of whom 26
required surgery for their continence and 12 required revision surgery. At the follow-up, 15 patients were
continent and voided using the neourethra. Out of 30 patients from the study, 17 patients expressed