Page 58 - Read Online
P. 58
Page 6 of 10 Somenek. Plast Aesthet Res 2022;9:16 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2021.84
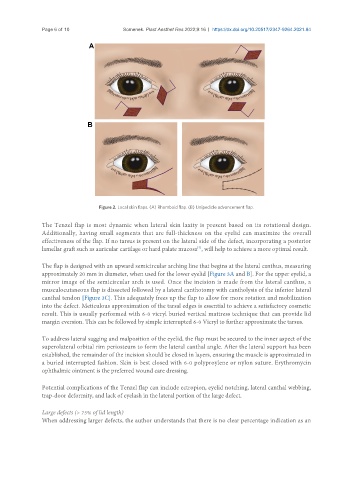
Figure 2. Local skin flaps. (A) Rhomboid flap. (B) Unipedicle advancement flap.
The Tenzel flap is most dynamic when lateral skin laxity is present based on its rotational design.
Additionally, having small segments that are full-thickness on the eyelid can maximize the overall
effectiveness of the flap. If no tarsus is present on the lateral side of the defect, incorporating a posterior
[7]
lamellar graft such as auricular cartilage or hard palate mucosa , will help to achieve a more optimal result.
The flap is designed with an upward semicircular arching line that begins at the lateral canthus, measuring
approximately 20 mm in diameter, when used for the lower eyelid [Figure 3A and B]. For the upper eyelid, a
mirror image of the semicircular arch is used. Once the incision is made from the lateral canthus, a
musculocutaneous flap is dissected followed by a lateral canthotomy with cantholysis of the inferior lateral
canthal tendon [Figure 3C]. This adequately frees up the flap to allow for more rotation and mobilization
into the defect. Meticulous approximation of the tarsal edges is essential to achieve a satisfactory cosmetic
result. This is usually performed with 6-0 vicryl buried vertical mattress technique that can provide lid
margin eversion. This can be followed by simple interrupted 6-0 Vicryl to further approximate the tarsus.
To address lateral sagging and malposition of the eyelid, the flap must be secured to the inner aspect of the
superolateral orbital rim periosteum to form the lateral canthal angle. After the lateral support has been
established, the remainder of the incision should be closed in layers, ensuring the muscle is approximated in
a buried interrupted fashion. Skin is best closed with 6-0 polyproylene or nylon suture. Erythromycin
ophthalmic ointment is the preferred wound care dressing.
Potential complications of the Tenzel flap can include ectropion, eyelid notching, lateral canthal webbing,
trap-door deformity, and lack of eyelash in the lateral portion of the large defect.
Large defects (> 75% of lid length)
When addressing larger defects, the author understands that there is no clear percentage indication as an