Page 89 - Read Online
P. 89
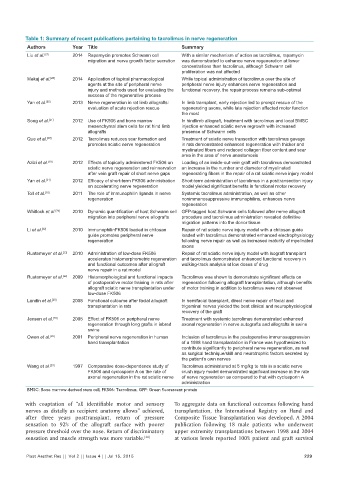
Table 1: Summary of recent publications pertaining to tacrolimus in nerve regeneration
Authors Year Title Summary
Liu et al. [27] 2014 Rapamycin promotes Schwann cell With a similar mechanism of action as tacrolimus, rapamycin
migration and nerve growth factor secretion was demonstrated to enhance nerve regeneration at lower
concentrations than tacrolimus, although Schwann cell
proliferation was not affected
Mekaj et al. [28] 2014 Application of topical pharmacological While topical administration of tacrolimus over the site of
agents at the site of peripheral nerve peripheral nerve injury enhances nerve regeneration and
injury and methods used for evaluating the functional recovery, the repair process remains sub-optimal
success of the regenerative process
Yan et al. [25] 2013 Nerve regeneration in rat limb allografts: In limb transplant, early rejection led to prompt rescue of the
evaluation of acute rejection rescue regenerating axons, while late rejection affected motor function
the most
Song et al. [21] 2012 Use of FK506 and bone marrow In hindlimb allograft, treatment with tacrolimus and local BMSC
mesenchymal stem cells for rat hind limb injection enhanced sciatic nerve regrowth with increased
allografts presence of Schwann cells
Que et al. [29] 2012 Tacrolimus reduces scar formation and Treatment of sciatic nerve transection with tacrolimus gavage
promotes sciatic nerve regeneration in rats demonstrated enhanced regeneration with thicker and
myelinated fibers and reduced collagen fiber content and scar
area in the area of nerve anastomosis
Azizi et al. [30] 2012 Effects of topically administered FK506 on Loading of an inside-out-vein graft with tacrolimus demonstrated
sciatic nerve regeneration and reinnervation an increase in the number and diameter of myelinated
after vein graft repair of short nerve gaps regenerating fibers in the repair of a rat sciatic nerve injury model
Yan et al. [31] 2012 Efficacy of short-term FK506 administration Short-term administration of tacrolimus in a posttransection injury
on accelerating nerve regeneration model yielded significant benefits in functional motor recovery
Toll et al. [18] 2011 The role of immunophilin ligands in nerve Systemic tacrolimus administration, as well as other
regeneration nonimmunosuppressive immunophilins, enhances nerve
regeneration
Whitlock et al. [24] 2010 Dynamic quantification of host Schwann cell GFP-tagged host Schwann cells followed after nerve allograft
migration into peripheral nerve allografts procedure and tacrolimus administration revealed definitive
migration patterns into the donor tissue
Li et al. [32] 2010 ImmunophilinFK506 loaded in chitosan Repair of rat sciatic nerve injury model with a chitosan guide
guide promotes peripheral nerve loaded with tacrolimus demonstrated enhanced electrophysiology
regeneration following nerve repair as well as increased maturity of myelinated
axons
Rustemeyer et al. [33] 2010 Administration of low-dose FK506 Repair of rat sciatic nerve injury model with isograft transplant
accelerates histomorphometric regeneration and tacrolimus demonstrated enhanced functional recovery in
and functional outcomes after allograft walking-track analysis at low doses of drug
nerve repair in a rat model
Rustemeyer et al. [22] 2009 Histomorphological and functional impacts Tacrolimus was shown to demonstrate significant effects on
of postoperative motor training in rats after regeneration following allograft transplantation, although benefits
allograft sciatic nerve transplantation under of motor training in addition to tacrolimus were not observed
low-dose FK506
Landin et al. [20] 2008 Functional outcome after facial allograft In hemifacial transplant, direct nerve repair of facial and
transplantation in rats trigeminal nerves yielded the best clinical and neurophysiological
recovery of the graft
Jensen et al. [19] 2005 Effect of FK506 on peripheral nerve Treatment with systemic tacrolimus demonstrated enhanced
regeneration through long grafts in inbred axonal regeneration in nerve autografts and allografts in swine
swine
Owen et al. [26] 2001 Peripheral nerve regeneration in human Inclusion of tacrolimus in the postoperative immunosuppression
hand transplantation of a 1998 hand transplantation in France was hypothesized to
contribute significantly to peripheral nerve regeneration, as well
as surgical technique/skill and neurotrophic factors secreted by
the patient’s own nerves
Wang et al. [23] 1997 Comparative dose-dependence study of Tacrolimus administered at 5 mg/kg to rats in a sciatic nerve
FK506 and cyclosporin A on the rate of crush injury model demonstrated significant increase in the rate
axonal regeneration in the rat sciatic nerve of nerve regeneration as compared to that with cyclosporin A
administration
BMSC: Bone marrow‑derived stem cell, FK506: Tacrolimus, GFP: Green fluorescent protein
with coaptation of “all identifiable motor and sensory To aggregate data on functional outcomes following hand
nerves as distally as recipient anatomy allows” achieved, transplantation, the International Registry on Hand and
after three years posttransplant, return of pressure Composite Tissue Transplantation was developed. A 2004
sensation to 92% of the allograft surface with poorer publication following 18 male patients who underwent
pressure threshold over the nose. Return of discriminatory upper extremity transplantations between 1998 and 2004
sensation and muscle strength was more variable. [34] at various levels reported 100% patient and graft survival
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 4 || Jul 15, 2015 229