Page 71 - Read Online
P. 71
Tang et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2024;11:61 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2024.117 Page 11 of 15
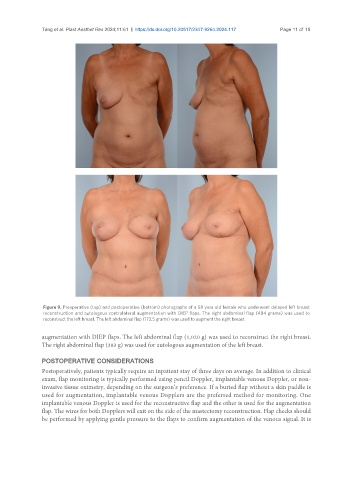
Figure 9. Preoperative (top) and postoperative (bottom) photographs of a 58 year old female who underwent delayed left breast
reconstruction and autologous contralateral augmentation with DIEP flaps. The right abdominal flap (484 grams) was used to
reconstruct the left breast. The left abdominal flap (173.5 grams) was used to augment the right breast.
augmentation with DIEP flaps. The left abdominal flap (1,020 g) was used to reconstruct the right breast.
The right abdominal flap (383 g) was used for autologous augmentation of the left breast.
POSTOPERATIVE CONSIDERATIONS
Postoperatively, patients typically require an inpatient stay of three days on average. In addition to clinical
exam, flap monitoring is typically performed using pencil Doppler, implantable venous Doppler, or non-
invasive tissue oximetry, depending on the surgeon’s preference. If a buried flap without a skin paddle is
used for augmentation, implantable venous Dopplers are the preferred method for monitoring. One
implantable venous Doppler is used for the reconstructive flap and the other is used for the augmentation
flap. The wires for both Dopplers will exit on the side of the mastectomy reconstruction. Flap checks should
be performed by applying gentle pressure to the flaps to confirm augmentation of the venous signal. It is