Page 46 - Read Online
P. 46
Page 8 of 11 Hara et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:42 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2023.11
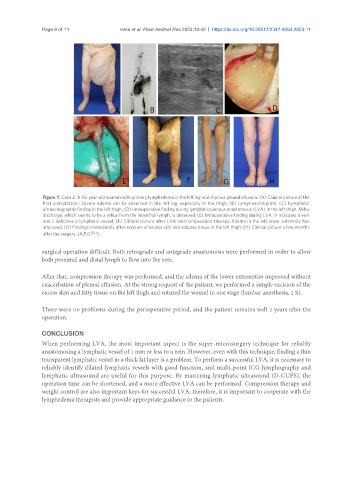
Figure 7. Case 2. A 92-year-old woman with primary lymphedema in the left leg and chylous pleural effusion. (A) Clinical picture at the
first consultation. Severe edema can be observed in the left leg, especially in the thigh; (B) Lymphoscintigram; (C) Lymphatic
ultrasonographic finding in the left thigh; (D) Intraoperative finding during lymphaticovenous anastomosis (LVA) in the left thigh. Milky
discharge, which seems to be a reflux from the intestinal lymph, is observed; (E) Intraoperative finding during LVA. V indicates a vein
and L indicates a lymphatic vessel; (F) Clinical picture after LVA and compression therapy. Edema in the left lower extremity has
improved; (G) Findings immediately after excision of excess skin and adipose tissue in the left thigh; (H) Clinical picture a few months
after the surgery. (A,F,G [52] ).
surgical operation difficult. Both retrograde and antegrade anastomosis were performed in order to allow
both proximal and distal lymph to flow into the vein.
After that, compression therapy was performed, and the edema of the lower extremities improved without
exacerbation of pleural effusion. At the strong request of the patient, we performed a simple excision of the
excess skin and fatty tissue on the left thigh and sutured the wound in one stage (lumbar anesthesia, 2 h).
There were no problems during the perioperative period, and the patient remains well 2 years after the
operation.
CONCLUSION
When performing LVA, the most important aspect is the super-microsurgery technique for reliably
anastomosing a lymphatic vessel of 1 mm or less to a vein. However, even with this technique, finding a thin
transparent lymphatic vessel in a thick fat layer is a problem. To perform a successful LVA, it is necessary to
reliably identify dilated lymphatic vessels with good function, and multi-point ICG lymphography and
lymphatic ultrasound are useful for this purpose. By mastering lymphatic ultrasound (D-CUPS), the
operation time can be shortened, and a more effective LVA can be performed. Compression therapy and
weight control are also important keys for successful LVA; therefore, it is important to cooperate with the
lymphedema therapists and provide appropriate guidance to the patients.