Page 43 - Read Online
P. 43
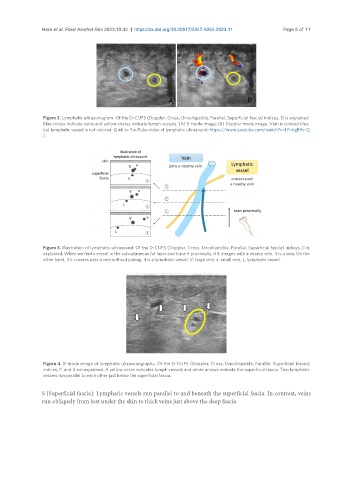
Hara et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:42 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2023.11 Page 5 of 11
Figure 2. Lymphatic ultrasonogram. Of the D-CUPS (Doppler, Cross, Uncollapsible, Parallel, Superficial fascia) indices, D is explained.
Blue circles indicate veins and yellow circles indicate lymph vessels. (A) B-mode image; (B) Doppler mode image. Vein is colored blue,
but lymphatic vessel is not colored. (Link to YouTube video of lymphatic ultrasound: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IYrxIgB9c-Q
).
Figure 3. Illustration of lymphatic ultrasound. Of the D-CUPS (Doppler, Cross, Uncollapsible, Parallel, Superficial fascia) indices, C is
explained. When we find a vessel in the subcutaneous fat layer and trace it proximally, if it merges with a nearby vein, it is a vein. On the
other hand, if it crosses past a vein without joining, it is a lymphatic vessel. V: large vein; v: small vein; L: lymphatic vessel.
Figure 4. B-mode image of lymphatic ultrasonography. Of the D-CUPS (Doppler, Cross, Uncollapsible, Parallel, Superficial fascia)
indices, P, and S are explained. A yellow circle indicates lymph vessels and white arrows indicate the superficial fascia. Two lymphatic
vessels run parallel to each other just below the superficial fascia.
S (Superficial fascia): Lymphatic vessels run parallel to and beneath the superficial fascia. In contrast, veins
run obliquely from just under the skin to thick veins just above the deep fascia.