Page 57 - Read Online
P. 57
Cevallos et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:30 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2023.01 Page 5 of 17
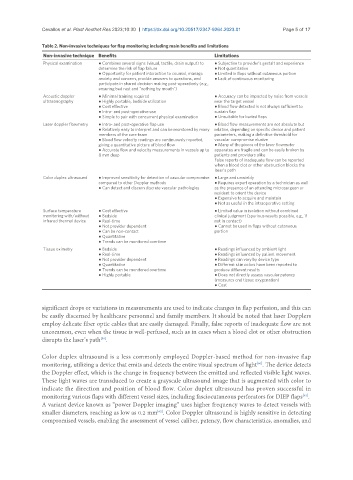
Table 2. Non-invasive techniques for flap monitoring including main benefits and limitations
Non-invasive technique Benefits Limitations
Physical examination ● Combines several signs (visual, tactile, drain output) to ● Subjective to provider’s gestalt and experience
determine the risk of flap failure ● Not quantitative
● Opportunity for patient interaction to counsel, manage ● Limited in flaps without cutaneous portion
anxiety and concern, provide answers to questions, and ● Lack of continuous monitoring
participate in shared decision making post-operatively (e.g.,
ensuring bed rest and “nothing by mouth”)
Acoustic doppler ● Minimal training required ● Accuracy can be impacted by noise from vessels
ultrasonography ● Highly portable, bedside utilization near the target vessel
● Cost effective ● Blood flow detected is not always sufficient to
● Intra- and post-operative use sustain flap
● Simple to pair with concurrent physical examination ● Unsuitable for buried flaps
Laser doppler flowmetry ● Intra- and post-operative flap use ● Blood flow measurements are not absolute but
● Relatively easy to interpret and can be monitored by many relative, depending on specific device and patient
members of the care team parameters, making a definitive threshold for
● Blood flow velocity readings are continuously reported, vascular compromise elusive
giving a quantitative picture of blood flow ● Many of the pieces of the laser flowmeter
● Accurate flow and velocity measurements in vessels up to apparatus are fragile and can be easily broken by
8 mm deep patients and providers alike
False reports of inadequate flow can be reported
when a blood clot or other obstruction blocks the
laser’s path
Color duplex ultrasound ● Improved sensitivity for detection of vascular compromise ● Large and unwieldy
compared to other Doppler methods ● Requires expert operation by a technician as well
● Can detect and discern discrete vascular pathologies as the presence of an attending microsurgeon or
resident to orient the device
● Expensive to acquire and maintain
● Not as useful in the intraoperative setting
Surface temperature ● Cost effective ● Limited value in isolation without combined
monitoring with/without ● Bedside clinical judgment (spurious results possible, e.g., if
infrared thermal device ● Real-time not in contact)
● Not provider dependent ● Cannot be used in flaps without cutaneous
● Can be non-contact portion
● Quantitative
● Trends can be monitored overtime
Tissue oximetry ● Bedside ● Readings influenced by ambient light
● Real-time ● Readings influenced by patient movement
● Not provider dependent ● Readings can vary by device type
● Quantitative ● Different skin colors have been reported to
● Trends can be monitored overtime produce different results
● Highly portable ● Does not directly assess vascular patency
(measures end tissue oxygenation)
● Cost
significant drops or variations in measurements are used to indicate changes in flap perfusion, and this can
be easily discerned by healthcare personnel and family members. It should be noted that laser Dopplers
employ delicate fiber optic cables that are easily damaged. Finally, false reports of inadequate flow are not
uncommon, even when the tissue is well-perfused, such as in cases when a blood clot or other obstruction
disrupts the laser’s path .
[50]
Color duplex ultrasound is a less commonly employed Doppler-based method for non-invasive flap
monitoring, utilizing a device that emits and detects the entire visual spectrum of light . The device detects
[60]
the Doppler effect, which is the change in frequency between the emitted and reflected visible light waves.
These light waves are transduced to create a grayscale ultrasound image that is augmented with color to
indicate the direction and position of blood flow. Color duplex ultrasound has proven successful in
[61]
monitoring various flaps with different vessel sizes, including fasciocutaneous perforators for DIEP flaps .
A variant device known as “power Doppler imaging” uses higher frequency waves to detect vessels with
smaller diameters, reaching as low as 0.2 mm . Color Doppler ultrasound is highly sensitive in detecting
[62]
compromised vessels, enabling the assessment of vessel caliber, patency, flow characteristics, anomalies, and