Page 61 - Read Online
P. 61
Al-Sammarraie et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2021;8:53-63 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2020.34 Page 57
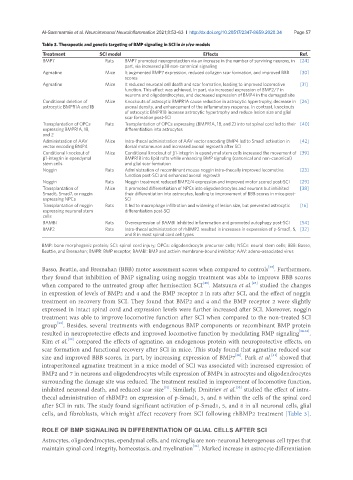
Table 3. Therapeutic and genetic targeting of BMP signaling in SCI in in vivo models
Treatment SCI model Effects Ref.
BMP7 Rats BMP7 promoted neuroprotection via an increase in the number of surviving neurons, in [24]
part, via increased p38 non-canonical signaling
Agmatine Mice It augmented BMP7 expression, reduced collagen scar formation, and improved BBB [30]
scores
Agmatine Mice It reduced neuronal cell death and scar formation, leading to improved locomotive [31]
function. This effect was achieved, in part, via increased expression of BMP2/7 in
neurons and oligodendrocytes, and decreased expression of BMP4 in the damaged site
Conditional deletion of Mice Knockouts of astrocytic BMPR1A cause reduction in astrocytic hypertrophy, decrease in [26]
astrocytic BMPR1A and 1B axonal density, and enhancement of the inflammatory response. In contrast, knockouts
of astrocytic BMPR1B increase astrocytic hypertrophy and reduce lesion size and glial
scar formation post-SCI
Transplantation of OPCs Rats Transplantation of OPCs expressing (BMPR1A, 1B, and 2) into rat spinal cord led to their [40]
expressing BMPR1A, 1B, differentiation into astrocytes
and 2
Administration of AAV Mice Intra-thecal administration of AAV vector encoding BMP4 led to Smad1 activation in [42]
vector encoding BMP4 dorsal motoneuron and increased axonal regrowth after SCI
Conditional knockout of Mice Conditional knockout of β1-integrin in ependymal stem cells increased the movement of [39]
β1-integrin in ependymal BMPR1B into lipid rafts while enhancing BMP signaling (canonical and non-canonical)
stem cells and glial scar formation
Noggin Rats Administration of recombinant mouse noggin intra-thecally improved locomotive [23]
function post-SCI and enhanced axonal regrowth
Noggin Rats Noggin treatment reduced BMP2/4 expression and improved motor scored post-SCI [29]
Transplantation of Mice It promoted differentiation of NPCs into oligodendrocytes and neurons but inhibited [38]
Smad6, Smad7, or noggin their differentiation into astrocytes, leading to improvement of BBB scores in mice post-
expressing NPCs SCI
Transplantation of noggin Rats It led to macrophage infiltration and widening of lesion size, but prevented astrocytic [16]
expressing neuronal stem differentiation post-SCI
cells
BAMBI Rats Overexpression of BAMBI inhibited inflammation and promoted autophagy post-SCI [54]
BMP2 Rats Intra-thecal administration of rhBMP2 resulted in increases in expression of p-Smad1, 5, [32]
and 8 in most spinal cord cell types
BMP: bone morphogenic protein; SCI: spinal cord injury; OPCs: oligodendrocyte precursor cells; NSCs: neural stem cells; BBB: Basso,
Beattie, and Bresnahan; BMPR: BMP receptor; BAMBI: BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor; AAV: adeno-associated virus
[29]
Basso, Beattie, and Bresnahan (BBB) motor assessment scores when compared to controls . Furthermore,
they found that inhibition of BMP signaling using noggin treatment was able to improve BBB scores
[29]
[23]
when compared to the untreated group after hemisection SCI . Matsuura et al. studied the changes
in expression of levels of BMP2 and 4 and the BMP receptor 2 in rats after SCI, and the effect of noggin
treatment on recovery from SCI. They found that BMP2 and 4 and the BMP receptor 2 were slightly
expressed in intact spinal cord and expression levels were further increased after SCI. Moreover, noggin
treatment was able to improve locomotive function after SCI when compared to the non-treated SCI
[23]
group . Besides, several treatments with endogenous BMP components or recombinant BMP protein
resulted in neuroprotective effects and improved locomotive function by modulating BMP signaling [30-32] .
[30]
Kim et al. compared the effects of agmatine, an endogenous protein with neuroprotective effects, on
scar formation and functional recovery after SCI in mice. This study found that agmatine reduced scar
[30]
[31]
size and improved BBB scores, in part, by increasing expression of BMP7 . Park et al. showed that
intraperitoneal agmatine treatment in a mice model of SCI was associated with increased expression of
BMP2 and 7 in neurons and oligodendrocytes while expression of BMP4 in astrocytes and oligodendrocytes
surrounding the damage site was reduced. The treatment resulted in improvement of locomotive function,
[31]
[32]
inhibited neuronal death, and reduced scar size . Similarly, Dmitriev et al. studied the effect of intra-
thecal administration of rhBMP2 on expression of p-Smad1, 5, and 8 within the cells of the spinal cord
after SCI in rats. The study found significant activation of p-Smad1, 5, and 8 in all neuronal cells, glial
cells, and fibroblasts, which might affect recovery from SCI following rhBMP2 treatment [Table 3].
ROLE OF BMP SIGNALING IN DIFFERENTIATION OF GLIAL CELLS AFTER SCI
Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglia are non-neuronal heterogenous cell types that
[33]
maintain spinal cord integrity, homeostasis, and myelination . Marked increase in astrocyte differentiation