Page 12 - Read Online
P. 12
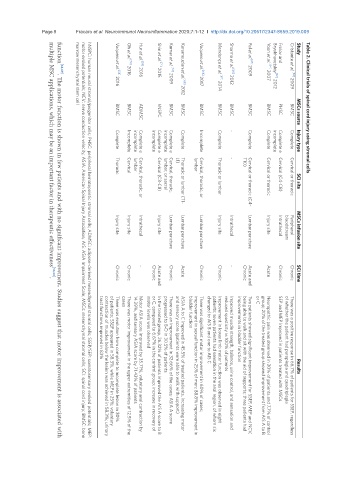
Page 8 Fracaro et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2020;7:1-12 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2019.009 Table 2. Clinical trials of spinal cord injury using stromal cells
Study
Frolov and
Oh et al. [72] 2016
Pal et al. [65] 2009
Shin et al. [71] 2015
Hur et al. [59] 2016
Yoon et al. [64] 2007
Kumar et al. [70] 2009
Sharma et al. [66] 2012
Vaquero et al. [68] 2017
Vaquero et al. [58] 2016
Bryukhovetskiy [57] 2012
Cristante et al. [63] 2009
Mendonça et al. [67] 2014
Karamouzian et al. [69] 2012
marrow mesenchymal stem cell
PHSC
BMSC
BMSC
BMSC
BMSC
BMSC
BMSC
BMSC
BMSC
BMSC
BMSC
hNSPC
ADMSC
MSCs source
-
Complete
Complete
Complete
Complete
Complete
Complete
Incomplete
incomplete
incomplete
incomplete
incomplete
Incomplete
Injury type
Complete e
Complete e
Complete e
Complete e
-
L1)
T10)
lumbar
lumbar
Cervical
Thoracic
SCI site
lumbar, or sacral
Cervical (C4-C8)
Cervical (C3-C8)
Cervical, thoracic,
Thoracic or lumbar
Cervical or thoracic
Cervical or thoracic
Cervical, thoracic, or
Cervical, thoracic, or
Thoracic or lumbar (T1-
Cervical or thoracic (C4–
Injury site
Injury site
Injury site
Injury site
Injury site
Peripheral
Intrathecal
Intrathecal
Intrathecal
bloodstream
Lumbar puncture
Lumbar puncture
MSCs infusion site
Lumbar puncture
Lumbar puncture
-
-
Acute
Acute
multiple MSC applications, which may be an important factor in therapeutic effectiveness [56,58] .
Chronic
Chronic
Chronic
Chronic
Chronic
Chronic
Chronic
Chronic
Chronic
SCI time
Acute and
Acute and
or C
cases
bladder function
motor levels was observed
tract functions improved in 83%
improvements in bladder function
changed to AIS B and one to AIS C
reduced spasticity in 100% of patients
progressed to B-D in 30.5% of patients
Results
SEP and MEP improved in patients treated with MSCs
of whether the patient had paraplegia and quadriplegia
14.29%, and sensory ASIA score by 71.43% of patients
There was significant motor improvement in 60% of cases;
and sensory score (patients were able to walk with support)
There was evolution from complete to incomplete lesion in 30%
Improvement in lower limb motor function was observed in eight
There was an improvement in 32.66% of the cases; ASIA A score
of patients; SSEP appeared in 58.3%, while MEP in 25%; voluntary
Improved muscle strength, balance, urine control, and sensation and
ASIA A to C improved in 45.5% of treated patients, increasing motor
or C, compared to 6.67% in the control group; increase in recovery of
Motor ASIA score improved by 35.71%, voluntary anal contraction by
being able to walk and sit with the aid of supports; three patients had
patients; seven patients had sensation in the anal region, of whom six
Neuropathic pain was observed in 20% of patients and 7.7% of control
In the treated group, 26.32% of patients improved the AIS A score to B
Two patients showed significant improvement for SSEP, MEP and NCV,
There was motor improvement in the upper extremities of 12.5% of the
improvement in sexual function in 25% of men; 88.8% improvement in
group; 20% of the treated group showed improvement from AIS A to B
There was a positive response in 66.7% of patients for SSEP, regardless
contraction of muscles below the lesion was achieved in 58.3%; urinary
function [68,69] . The motor function is shown in few patients and with no significant improvement. Studies suggest that motor improvement is associated with
hNSPC: human neural stromal/progenitor cells; PHSC: peripheral hematopoietic stromal cells; ADMSC: adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells; SSEP/SEP: somatosensory evoked potentials; MEP:
motor evoked potentials; NCV: nerve conduction velocity; ASIA: American Spinal Injury Association; AIS: ASIA Impairment Scale; MSCs: mesenchymal stromal cells; SCI: spinal cord injury; BMSC: bone