Page 57 - Read Online
P. 57
Page 6 of 16 Zhang et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2019;6:8 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2019.06
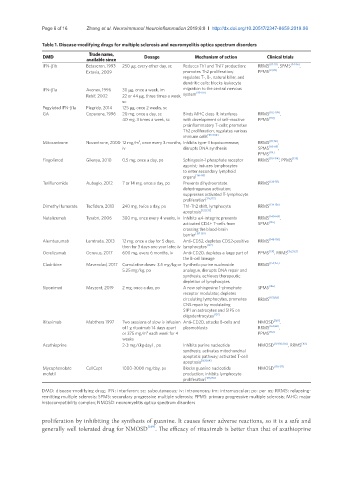
Table 1. Disease-modifying drugs for multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders
Trade name,
DMD available since Dosage Mechanism of action Clinical trials
IFN-β1b Betaseron, 1993 250 μg, every other day, sc Reduces Th1 and Th17 production; RRMS [87-93] , SPMS [94-96] ,
Extavia, 2009 promotes Th2 proliferation; PPMS [97,98]
regulates T-, B-, natural killer, and
dendritic cells; blocks leukocyte
IFN-β1a Avonex, 1996 30 μg, once a week, im migration to the central nervous
[99-101]
Rebif, 2002 22 or 44 μg, three times a week, system
sc
Pegylated IFN-β1a Plegridy, 2014 125 μg, once 2 weeks, sc
GA Copaxone, 1996 20 mg, once a day, sc Binds MHC class II; interferes RRMS [105-109] ,
40 mg, 3 times a week, sc with development of self-reactive PPMS [110]
proinflammatory T-cells; promotes
Th2 proliferation; regulates various
immune cells [102-104]
Mitoxantrone Novantrone, 2000 12 mg/m , once every 3 months, Inhibits type-II topoisomerase; RRMS [111,112] ,
2
iv disrupts DNA synthesis SPMS [113-115] ,
PPMS [114]
Fingolimod Gilenya, 2010 0.5 mg, once a day, po Sphingosin-1 phosphate receptor RRMS [119-124] , PPMS [125]
agonist; induces lymphocytes
to enter secondary lymphoid
organs [116-118]
Teriflunomide Aubagio, 2012 7 or 14 mg, once a day, po Prevents dihydroorotate RRMS [128-131]
dehydrogenase activation;
suppresses activated T-lymphocyte
proliferation [126,127]
Dimethyl fumarate Tecfidera, 2013 240 mg, twice a day, po Th1-Th2 shift, lymphocyte RRMS [134-136]
apoptosis [132,133]
Natalizumab Tysabri, 2006 300 mg, once every 4 weeks, iv Inhibits α4-integrin; prevents RRMS [140-145] ,
activated CD4+ T-cells from SPMS [146]
crossing the blood-brain
barrier [137-139]
Alemtuzumab Lemtrada, 2013 12 mg, once a day for 5 days, Anti-CD52; depletes CD52-positive RRMS [148-150]
then for 3 days one year later, iv lymphocytes [147]
Ocrelizumab Ocrevus, 2017 600 mg, every 6 months, iv Anti-CD20, depletes a large part of PPMS [151] , RRMS [152,153]
the B-cell lineage
Cladribine Mavenclad, 2017 Cumulative doses: 3.5 mg/kg or Synthetic purine nucleoside RRMS [154,155]
5.25 mg/kg, po analogue, disrupts DNA repair and
synthesis, achieves therapeutic
depletion of lymphocytes
Siponimod Mayzent, 2019 2 mg, once a day, po A new sphingosine 1-phosphate SPMS [156]
receptor modulator, depletes
circulating lymphocytes, promotes RRMS [157,158]
CNS repair by modulating
S1P1 on astrocytes and S1P5 on
oligodentrocytes [157]
Rituximab Mabthera 1997 Two sessions of slow iv infusion Anti-CD20, attacks B-cells and NMOSD [159] ,
of 1 g rituximab 14 days apart plasmoblasts RRMS [160,161] ,
2
or 375 mg/m each week for 4 PPMS [162]
weeks
Azathioprine 2-3 mg/(kg·day) , po Inhibits purine nucleotide NMOSD [159,165,166] , RRMS [167]
synthesis; activates mitochondrial
apoptotic pathway; activated T-cell
apoptosis [163,164]
Mycophenolate CellCept 1000-3000 mg/day, po Blocks guanine nucleotide NMOSD [170-172]
mofetil production; inhibits lymphocyte
proliferation [168,169]
DMD: disease-modifying drug; IFN: interferon; sc: subcutaneous; iv: intravenous; im: intramuscular; po: per os; RRMS: relapsing-
remitting multiple sclerosis; SPMS: secondary progressive multiple sclerosis; PPMS: primary progressive multiple sclerosis; MHC: major
histocompatibility complex; NMOSD: neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders
proliferation by inhibiting the synthesis of guanine. It causes fewer adverse reactions, so it is a safe and
generally well tolerated drug for NMOSD [169] . The efficacy of rituximab is better than that of azathioprine