Page 100 - Read Online
P. 100
Page 22 of 32 Noor et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2019;6:10 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2019.18
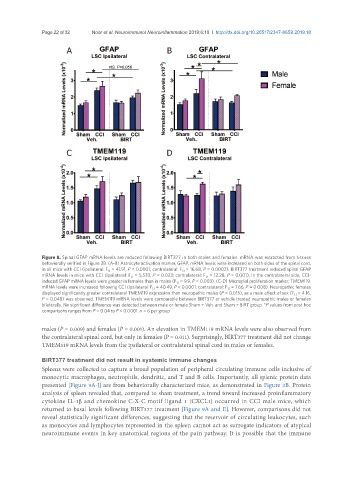
A B
C D
Figure 8. Spinal GFAP mRNA levels are reduced following BIRT377 in both males and females. mRNA was extracted from tissues
behaviorally verified in Figure 2B. (A-B) Astrocyte activation marker, GFAP, mRNA levels were increased on both sides of the spinal cord,
in all mice with CCI (ipsilateral: F 1,1 = 41.91, P < 0.0001; contralateral: F 1,1 = 16.68, P = 0.0002). BIRT377 treatment reduced spinal GFAP
mRNA levels in mice with CCI (ipsilateral: F 1,1 = 5.533, P = 0.023; contralateral: F 1,1 = 12.28, P = 0.001). In the contralateral side, CCI-
induced GFAP mRNA levels were greater in females than in males (F 1,1 = 9.9, P = 0.003). (C-D) Microglial proliferation marker, TMEM119,
mRNA levels were increased following CCI (ipsilateral: F 1,1 = 40.49, P < 0.0001; contralateral: F 1,1 = 7.66, P = 0.008). Neuropathic females
displayed significantly greater contralateral TMEM119 expression than neuropathic males (P = 0.015), as a main effect of sex (F 1,1 = 4.16,
P = 0.048) was observed. TMEM119 mRNA levels were comparable between BIRT377 or vehicle treated neuropathic males or females
bilaterally. No significant difference was detected between male or female Sham + Veh. and Sham + BIRT group. *P values from post hoc
comparisons ranges from P = 0.04 to P < 0.0001. n = 6 per group
males (P = 0.009) and females (P = 0.001). An elevation in TMEM119 mRNA levels were also observed from
the contralateral spinal cord, but only in females (P = 0.011). Surprisingly, BIRT377 treatment did not change
TMEM119 mRNA levels from the ipsilateral or contralateral spinal cord in males or females.
BIRT377 treatment did not result in systemic immune changes
Spleens were collected to capture a broad population of peripheral circulating immune cells inclusive of
monocytic macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic, and T and B cells. Importantly, all splenic protein data
presented [Figure 9A-J] are from behaviorally characterized mice, as demonstrated in Figure 2B. Protein
analysis of spleen revealed that, compared to sham treatment, a trend toward increased proinflammatory
cytokine IL-1β and chemokine C-X-C motif ligand 1 (CXCL1) occurred in CCI male mice, which
returned to basal levels following BIRT377 treatment [Figure 9A and E]. However, comparisons did not
reveal statistically significant differences, suggesting that the reservoir of circulating leukocytes, such
as monocytes and lymphocytes represented in the spleen cannot act as surrogate indicators of atypical
neuroimmune events in key anatomical regions of the pain pathway. It is possible that the immune