Page 157 - Read Online
P. 157
Kafle et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2018;5:24 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2018.10 Page 3 of 8
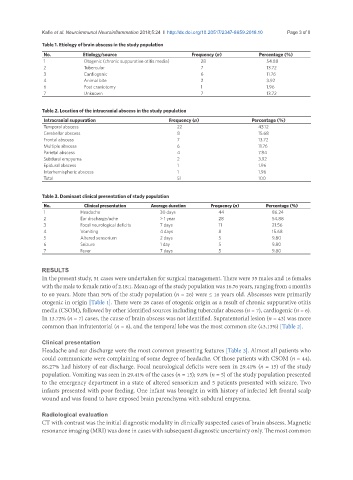
Table 1. Etiology of brain abscess in the study population
No. Etiology/source Frequency (n) Percentage (%)
1 Otogenic (chronic suppurative otitis media) 28 54.88
2 Tubercular 7 13.72
3 Cardiogenic 6 11.76
4 Animal bite 2 3.92
6 Post craniotomy 1 1.96
7 Unknown 7 13.72
Table 2. Location of the intracranial abscess in the study population
Intracranial suppuration Frequency (n) Percentage (%)
Temporal abscess 22 43.12
Cerebellar abscess 8 15.68
Frontal abscess 7 13.72
Multiple abscess 6 11.76
Parietal abscess 4 7.84
Subdural empyema 2 3.92
Epidural abscess 1 1.96
Interhemispheric abscess 1 1.96
Total 51 100
Table 3. Dominant clinical presentation of study population
No. Clinical presentation Average duration Frequency (n) Percentage (%)
1 Headache 30 days 44 86.24
2 Ear discharge/ache > 1 year 28 54.88
3 Focal neurological deficits 7 days 11 21.56
4 Vomiting 4 days 8 15.68
5 Altered sensorium 2 days 5 9.80
6 Seizure 1 day 5 9.80
7 Fever 7 days 5 9.80
RESULTS
In the present study, 51 cases were undertaken for surgical management. There were 35 males and 16 females
with the male to female ratio of 2.18:1. Mean age of the study population was 16.76 years, ranging from 4 months
to 60 years. More than 50% of the study population (n = 26) were ≤ 16 years old. Abscesses were primarily
otogenic in origin [Table 1]. There were 28 cases of otogenic origin as a result of chronic suppurative otitis
media (CSOM), followed by other identified sources including tubercular abscess (n = 7), cardiogenic (n = 6).
In 13.72% (n = 7) cases, the cause of brain abscess was not identified. Supratentorial lesion (n = 43) was more
common than infratentorial (n = 8), and the temporal lobe was the most common site (43.13%) [Table 2].
Clinical presentation
Headache and ear discharge were the most common presenting features [Table 3]. Almost all patients who
could communicate were complaining of some degree of headache. Of those patients with CSOM (n = 44),
86.27% had history of ear discharge. Focal neurological deficits were seen in 29.41% (n = 15) of the study
population. Vomiting was seen in 29.41% of the cases (n = 15); 9.8% (n = 5) of the study population presented
to the emergency department in a state of altered sensorium and 5 patients presented with seizure. Two
infants presented with poor feeding. One infant was brought in with history of infected left frontal scalp
wound and was found to have exposed brain parenchyma with subdural empyema.
Radiological evaluation
CT with contrast was the initial diagnostic modality in clinically suspected cases of brain abscess. Magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI) was done in cases with subsequent diagnostic uncertainty only. The most common