Page 88 - Read Online
P. 88
Chen et al. Anti-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor autoimmune encephalitis with sensory attack
DISCUSSION this one, only present with nonspecific background
change or diffuse slow waves, especially at the early
Anti-NMDAR encephalitis is a type of limbic encephalitis stage of disease. Usually, bilateral medial temporal
[5]
that is typically found in young women with teratomas. lobe signal change on MRI scans raise suspicions for
[2]
This kind of encephalitis is usually subacute at onset limbic encephalitis. However, normal MRI results
[6]
with significant psychiatric symptoms, including cannot exclude the diagnosis. Our patient underwent
agitation, mania, hallucination, aggression as well as 3T cranial MRI scans twice, and no obvious change
cognitive dysfunction. Some patients will develop was found, including in the limbic system. It is known
[3]
echolalia, echoapraxia, involuntary movements, such that, although NMDARs are more concentrated in
as stereotype, central hypoventilation, and autonomic the hippocampal area, they also can be found in
instability, which have been considered more specific many other areas of the brain, including sensory and
characteristics for helping in diagnosis. Although association cortex and subcortical regions. The
[4]
[7]
extreme delta brush on an EEG can be another widespread distribution of the receptor in cortical
specific diagnostic marker, most patients, including regions could explain the diffuse slow waves on the
EEGs and the persistent sensory symptoms seen in
our patient. Oral-facial dyskinesias indicated basal
ganglion involvement. Although most anti-NMDAR
encephalitis is limbic, some patients may have more
extensive lesions, including cortical and subcortical;
thus, limbic encephalitis is not always only limbic.
Likewise, an FDG-PET scan of our patient showed
hypo-metabolism in multiple brain regions. In addition,
not all patients have positive MRI findings, especially at
the early stage of disease, and we speculated that MRI
scanning may not always be reliable for early diagnosis
and differentiation. The differential diagnosis of anti-
NMDAR encephalitis, excluded HSV encephalitis, CMV
encephalitis, Hashimoto’s encephalopathy, systemic
lupus erythematosus encephalopathy, antiphospholipid
antibody syndrome, Sjögren’s syndrome, and primary
central nervous angiitis. We also tested for anti-AQP4
[8]
to exclude its co-occurrence with anti-NMDAR. [9,10] This
patient was steroid unresponsive, since a high dose of
intravenous administration of steroids failed to improve
her symptoms. After IVIG infusion and tumor resection,
she recovered to normal status in a short period of time,
and we gradually tapered down all her medications.
This patient did not show any relapse 1 year after
discharge. Although most studies indicated recovery
was a slow process for anti-NMDAR encephalitis,
our experience in patient with teratoma and receiving
tumor resection, had good prognosis and fast recovery
time. In addition, these patients are not suggested to
continue long-time immunosuppressant.
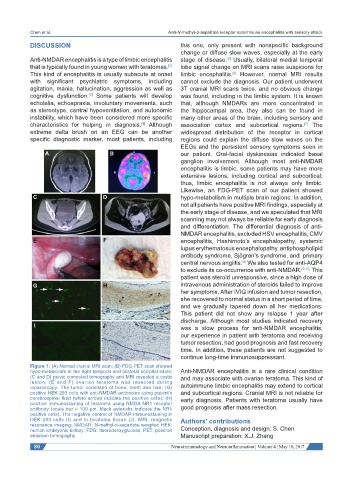
Figure 1: (A) Normal cranial MRI scan; (B) FDG-PET scan showed
hypo-metabolism in the right temporal and bilateral occipital lobes; Anti-NMDAR encephalitis is a rare clinical condition
(C and D) pelvic computed tomography and MRI revealed a cystic and may associate with ovarian teratoma. This kind of
lesion; (E and F) ovarian teratoma was resected during
laparoscopy. The tumor consisted of bone, teeth and hair; (G) autoimmune limbic encephalitis may extend to cortical
positive HEK 293 cells with anti-NMDAR antibodies using patient’s and subcortical regions. Cranial MRI is not reliable for
cerebrospinal fluid (white arrows indicate the positive cells); (H) early diagnosis. Patients with teratoma usually have
positive immunostaining of teratoma using NMDA NR1 receptor
antibody (scale bar = 100 μm, black asterisks indicate the NR1 good prognosis after mass resection.
positive cells). The negative control of NMDAR immunostaining in
HEK 293 cells (I) and in teratoma tissue (J). MRI: magnetic Authors’ contributions
resonance imaging; NMDAR: N-methyl-d-aspartate-receptor; HEK:
human embryonic kidney; FDG: fluorodeoxyglucose; PET: positron Conception, diagnosis and design: S. Chen
emission tomography Manuscript preparation: X.J. Zhang
80 Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 4 ¦ May 10, 2017