Page 90 - Read Online
P. 90
catatonic schizophrenia. These symptoms alternate infection which later precipitate autoimmune disease.
with periods of agitation. Some patients develop
bizarre and inappropriate behavior such as smiling, Psychiatric symptoms
echophenomenal (both words and movement), or The psychiat ric sy mptoms of a nti‑N M DA R
[11]
catalepsy‑like symptoms. Dissociative (paradoxical) encephalitis encompass a broad spectrum that
responses to stimuli (unresponsive to painful stimuli, includes anxiety, depression, agitation, abnormal
but resistant to eye opening) are often presented behavior, delusion, hallucination, mania, and frank
in patients, mimicking a psychogenic condition or psychosis. [13] The symptoms usually present at the
malingering. Most patients later develop hyperkinetic beginning of the disease, leading to medical attention
abnormal movements, the majority of which are (mostly by a psychiatrist). It is the most common
oro‑lingual‑facial dyskinesia; however, other types initial manifestation in both sexes. [15] In younger
of movement may also be observed. During the same children, parents may describe the symptoms as
period, autonomic instability and hypoventilation temper tantrums, behavioral changes, aggression,
[16]
also occur. The autonomic manifestations include and progressive speech deterioration. Staff phobia
[16]
hyperthermia, tachy‑bradycardia, and labile blood has also been reported in children or adolescents.
pressure. Autonomic dysfunction leads to a prolonged Overall, the psychiatric symptoms associated with
cardiac pause and requires a temporary pacemaker. the initial manifestation or during relapses are the
[17]
Hypoventilation can present alone or in association same in both sexes and all ages. Isolated psychiatric
with autonomic instability, which necessitates symptoms can be observed in up to 4% of patients
[17]
respiratory support. This phenomenon often occurs (either at disease onset or during relapses). These
during the period of hyperkinetic movement, or it can symptoms may be explained by reduced NMDAR
occur during early stages of symptoms. Within 4 weeks synaptic content and disruption of receptor function
of symptom onset, most patients develop a similar in discrete regions of the brain. NMDARs are widely
[14]
spectrum of symptoms irrespective of their age. The expressed throughout the entire brain, and, therefore,
characteristics of classical anti‑NMDAR encephalitis the density of receptor expression or the susceptibility
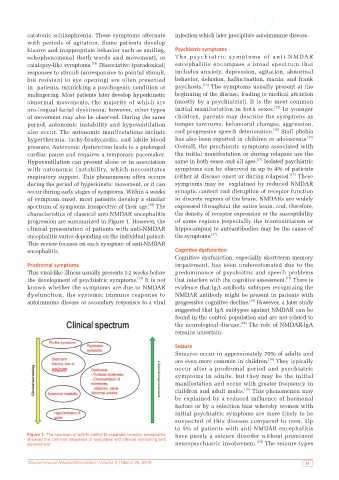
progression are summarized in Figure 1. However, the of some regions (especially the frontostriatum or
clinical presentation of patients with anti‑NMDAR hippocampus) to autoantibodies may be the cause of
encephalitis varies depending on the individual patient. the symptoms. [17]
This review focuses on each symptom of anti‑NMDAR
encephalitis. Cognitive dysfunction
Cognitive dysfunction, especially short‑term memory
Prodromal symptoms impairment, has been underestimated due to the
This viral‑like illness usually presents 1‑2 weeks before predominance of psychiatric and speech problems
[13]
[11]
the development of psychiatric symptoms. It is not that interfere with the cognitive assessment. There is
known whether the symptoms are due to NMDAR evidence that IgA antibody subtypes recognizing the
dysfunction, the systemic immune response to NMDAR antibody might be present in patients with
[18]
autoimmune disease or secondary responses to a viral progressive cognitive decline. However, a later study
suggested that IgA subtypes against NMDAR can be
found in the control population and are not related to
[19]
the neurological disease. The role of NMDAR‑IgA
remains uncertain.
Seizure
Seizures occur in approximately 70% of adults and
[14]
are even more common in children. They typically
occur after a prodromal period and psychiatric
symptoms in adults, but they may be the initial
manifestation and occur with greater frequency in
[15]
children and adult males. This phenomenon may
be explained by a reduced influence of hormonal
factors or by a selection bias whereby women with
initial psychiatric symptoms are more likely to be
suspected of this disease compared to men. Up
to 5% of patients with anti‑NMDAR encephalitis
Figure 1: The spectrum of anti‑N‑methyl‑D‑aspartate receptor encephalitis have purely a seizure disorder without prominent
showing the common sequence of symptoms with clinical worsening and [20]
improvement neuropsychiatric involvement. The seizure types
Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 3 | March 28, 2016 81