Page 158 - Read Online
P. 158
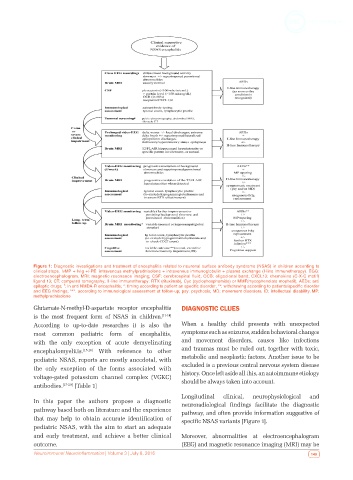
Figure 1: Diagnostic investigations and treatment of encephalitis related to neuronal surface antibody syndrome (NSAS) in children according to
clinical steps. IvMP + IvIg +/-PE: intravenous methylprednisolone + intravenous immunoglobulin + plasma exchange (I-line immunotherapy). EGG:
electroencephalogram; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; OCB: oligoclonal band; CXCL13: chemokine (C-X-C motif)
ligand 13; CT: computed tomography; II-line immunotherapy: RTX (rituximab), Cyc (cyclophosphamide) or MMF(mycophenolate mophetil); AEDs: anti
#
epileptic drugs; : in anti NMDA-R encephalitis; *: timing according to patient an specific disorder; **: withdrawing according to patients/specific disorder
and EEG findings; ***: according to immunological assessment at follow-up; psy: psychosis; MD: movement disorders; ID: intellectual disability; MP:
methylprednisolone
Glutamate-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis DIAGNOSTIC CLUES
is the most frequent form of NSAS in children. [11-14]
According to up-to-date researches it is also the When a healthy child presents with unexpected
most common pediatric form of encephalitis, symptoms such as seizures, sudden behavioral changes
with the only exception of acute demyelinating and movement disorders, causes like infections
encephalomyelitis. [15,16] With reference to other and traumas must be ruled out, together with toxic,
pediatric NSAS, reports are mostly anecdotal, with metabolic and neoplastic factors. Another issue to be
the only exception of the forms associated with excluded is a previous central nervous system disease
history. Once left aside all this, an autoimmune etiology
voltage-gated potassium channel complex (VGKC) should be always taken into account.
antibodies. [17-20] [Table 1]
Longitudinal clinical, neurophysiological and
In this paper the authors propose a diagnostic
neuroradiological findings facilitate the diagnostic
pathway based both on literature and the experience pathway, and often provide information suggestive of
that may help to obtain accurate identification of specific NSAS variants [Figure 1].
pediatric NSAS, with the aim to start an adequate
and early treatment, and achieve a better clinical Moreover, abnormalities at electroencephalogram
outcome. (EEG) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be
Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 3 | July 8, 2016 149