Page 86 - Read Online
P. 86
RESULTS
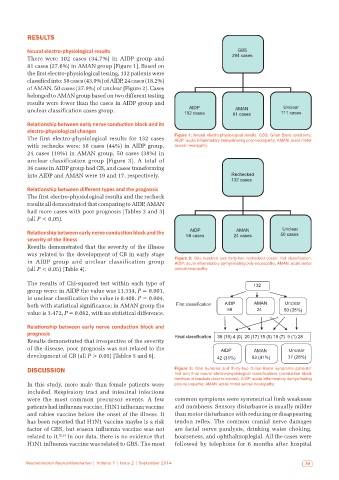
Neural electro‑physiological results *%6
There were 102 cases (34.7%) in AIDP group and FDVHV
81 cases (27.6%) in AMAN group [Figure 1]. Based on
the first electro-physiological testing, 132 patients were
classified into: 58 cases (43.9%) of AIDP, 24 cases (18.2%)
of AMAN, 50 cases (37.9%) of unclear [Figure 2]. Cases
belonged to AMAN group based on two different testing
results were fewer than the cases in AIDP group and
$,'3
8QFOHDU
$0$1
unclear classification cases group. FDVHV FDVHV FDVHV
Relationship between early nerve conduction block and its
electro‑physiological changes
The first electro-physiological results for 132 cases Figure 1: Neural electro‑physiological results. GBS: Gillan‑Barre syndrome;
AIDP: acute inflammatory demyelinating poly-neuropathy; AMAN: acute motor
with rechecks were: 58 cases (44%) in AIDP group, axonal neuropathy
24 cases (18%) in AMAN group, 50 cases (38%) in
unclear classification group [Figure 3]. A total of
36 cases in AIDP group had CB, and cases transforming
into AIDP and AMAN were 19 and 17, respectively. 5HFKHFNHG
FDVHV
Relationship between different types and the prognosis
The first electro-physiological results and the recheck
results all demonstrated that comparing to AIDP, AMAN
had more cases with poor prognosis [Tables 2 and 3]
(all P < 0.05).
8QFOHDU
$0$1
$,'3
Relationship between early nerve conduction block and the FDVHV FDVHV FDVHV
severity of the illness
Results demonstrated that the severity of the illness
was related to the development of CB in early stage
in AIDP group and unclear classification group Figure 2: One hundred and thirty-two rechecked cases’ first classification.
AIDP: acute inflammatory demyelinating poly-neuropathy; AMAN: acute motor
(all P < 0.05) [Table 4]. axonal neuropathy
The results of Chi-squared test within each type of
group were: in AIDP the value was 11.334, P = 0.001,
in unclear classification the value is 8.408, P = 0.004,
both with statistical significance; in AMAN group the )LUVW FODVVLILFDWLRQ $,'3 $0$1 8QFOHDU
value is 3.472, P = 0.062, with no statistical difference.
Relationship between early nerve conduction block and
prognosis )LQDO FODVVLILFDWLRQ
Results demonstrated that irrespective of the severity
of the disease, poor prognosis was not related to the $,'3 $0$1 8QFOHDU
development of CB (all P > 0.05) [Tables 5 and 6].
DISCUSSION Figure 3: One hundred and thirty‑two Gillan‑Barre syndrome patients’
first and final neural electro-physiological classifications (conduction block
numbers in brackets clear to arrows). AIDP: acute inflammatory demyelinating
In this study, more male than female patients were poly‑neuropathy; AMAN: acute motor axonal neuropathy
included. Respiratory tract and intestinal infections
were the most common precursor events. A few common symptoms were symmetrical limb weakness
patients had influenza vaccine, H1N1 influenza vaccine and numbness. Sensory disturbance is usually milder
and rabies vaccine before the onset of the illness. It than motor disturbance with reducing or disappearing
has been reported that H1N1 vaccine maybe is a risk tendon reflex. The common cranial nerve damages
factor of GBS, but season influenza vaccine was not are facial nerve paralysis, drinking water choking,
related to it. [5,6] In our data, there is no evidence that hoarseness, and ophthalmoplegial. All the cases were
H1N1 influenza vaccine was related to GBS. The most followed by telephone for 6 months after hospital
Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 2 | September 2014 79