Page 61 - Read Online
P. 61
Table 1: MicroRNAs and their targets in Hh signaling glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) and casein kinase
pathway 1 (CK1). It has been observed that molecules involved
MicroRNA Target in Wnt signaling, such as GSK-3 β, regulate the Hh
miR‑302~367 CXCR4 Shh‑Gli‑Nanog signaling pathway. [51] In turn, activation of Gli may
miR‑125b Smo stimulate the transcription of Wnt ligands. It has been
miR‑326 Smo, Gli2 found that GSK-3 β phosphorylates and stabilizes Sufu,
miR‑324‑5p Smo, Gli1
miR‑214 Sufu leading to inhibition of Hh activation. [52] Moreover,
miR‑941 Smo, Sufu, Gli1 the Hh pathway was found to inhibit Wnt signaling,
miR‑212 Ptch1 as a result, of Gli1 induction through up-regulation of
Hh: Hedgehog; Shh: sonic Hedgehog; Ptch: patched; Smo: smoothened;
Sufu: suppressor of fused secreted frizzled-related protein 1. [53]
Notch signaling is another conserved developmental
signaling pathway that is important for embryogenesis,
cellular homeostasis and stem cell renewal. [54] Notch
receptor activation induces the expression of hairy
and enhancer of split 3 (Hes3) and Shh through
rapid activation of cytoplasmic signals, including
the serine/threonine kinase Akt, the transcription
factor STAT3, and the mammalian target of
rapamycin (mTOR), leading to the promotion of NSC
survival. Simultaneously, Shh induces the expression
[55]
of another specific target gene, Hes1, and Smo function
has been found to be necessary for Shh-induced up-
regulation of Hes1. [56] Moreover, inhibition of Shh and
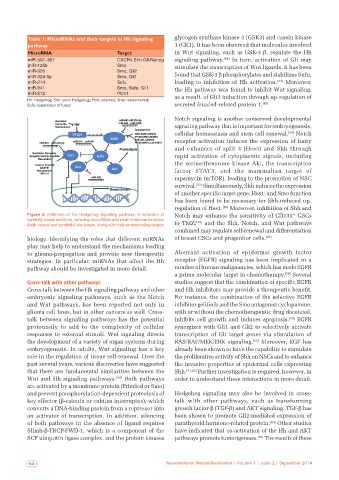
Figure 2: Inhibition of the Hedgehog signaling pathway. A selection of Notch may enhance the sensitivity of CD133 GSCs
+
currently known inhibitors, including microRNAs and small molecular inhibitors to TMZ; [38] and the Shh, Notch, and Wnt pathways
(both natural and synthetic) are shown, along with their corresponding targets
combined may regulate self-renewal and differentiation
biology. Identifying the roles that different miRNAs of breast CSCs and progenitor cells. [57]
play may help to understand the mechanisms leading
to glioma-propagation and provide new therapeutic Aberrant activation of epidermal growth factor
strategies. In particular, miRNAs that affect the Hh receptor (EGFR) signaling has been implicated in a
pathway should be investigated in more detail. number of human malignancies, which has made EGFR
a prime molecular target in chemotherapy. [58] Several
Cross‑talk with other pathways studies suggest that the combination of specific EGFR
Cross-talk between the Hh signaling pathway and other and Hh inhibitors may provide a therapeutic benefit.
embryonic signaling pathways, such as the Notch For instance, the combination of the selective EGFR
and Wnt pathways, has been reported not only in inhibitor gefitinib and the Smo antagonist cyclopamine,
glioma cell lines, but in other cancers as well. Cross- with or without the chemotherapeutic drug docetaxel,
talk between signaling pathways has the potential inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis. [59] EGFR
profoundly to add to the complexity of cellular synergizes with Gli1 and Gli2 to selectively activate
responses to external stimuli. Wnt signaling directs transcription of Gli target genes via stimulation of
the development of a variety of organ systems during RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling. [60] Moreover, EGF has
embryogenesis. In adults, Wnt signaling has a key already been shown to have the capability to stimulate
role in the regulation of tissue self-renewal. Over the the proliferative activity of Shh on NSCs and to enhance
past several years, various discoveries have suggested the invasive properties of epidermal cells expressing
that there are fundamental similarities between the Shh. [61,62] Further investigation is required, however, in
Wnt and Hh signaling pathways. [50] Both pathways order to understand these interactions in more detail.
are activated by a membrane protein (Frizzled or Smo)
and prevent phosphorylation-dependent proteolysis of Hedgehog signaling may also be involved in cross-
key effector (β-catenin or cubitus interruptus), which talk with other pathways, such as transforming
converts a DNA-binding protein from a repressor into growth factor-β (TGF-β) and AKT signaling. TGF-β has
an activator of transcription. In addition, silencing been shown to promote Gli2-mediated expression of
of both pathways in the absence of ligand requires parathyroid hormone-related protein. [63] Other studies
Slimb-β-TRCP-FWD-1, which is a component of the have indicated that co-activation of the Hh and AKT
SCF ubiquitin ligase complex, and the protein kinases pathways promote tumorigenesis. The results of these
[64]
54 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 2 | September 2014