Page 55 - Read Online
P. 55
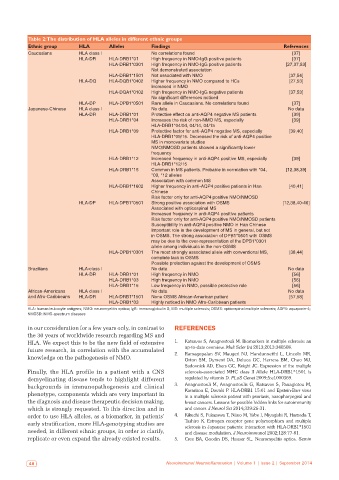
Table 2: The distribution of HLA alleles in different ethnic groups
Ethnic group HLA Alleles Findings References
Caucasians HLA class I No correlations found [37]
HLA‑DR HLA‑DRB1*01 High frequency in NMO‑IgG positive patients [37]
HLA‑DRB1*0301 High frequency in NMO‑IgG positive patients [27,37,53]
Not demonstrated association
HLA‑DRB1*1501 Not associated with NMO [37,54]
HLA‑DQ HLA‑DQB1*0402 Higher frequency in NMO compared to HCs [27,53]
Increased in NMO
HLA‑DQA1*0102 High frequency in NMO‑IgG negative patients [37,53]
No significant differences noticed
HLA‑DP HLA‑DPB1*0501 Rare allele in Caucasians. No correlations found [37]
Japanese‑Chinese HLA class I No data No data
HLA‑DR HLA‑DRB1*01 Protective effect on anti‑AQP4 negative MS patients [39]
HLA‑DRB1*04 Increases the risk of non‑NMO MS, especially [39]
HLA‑DRB1*04/04, 04/14, 04/15
HLA‑DRB1*09 Protective factor for anti‑AQP4 negative MS, especially [39,40]
HLA‑DRB1*09/15. Decreased the risk of anti‑AQP4 positive
MS in monovariate studies
NMO/NMOSD patients showed a significantly lower
frequency
HLA‑DRB1*12 Increased frequency in anti‑AQP4 positive MS, especially [39]
HLA‑DRB1*12/15
HLA‑DRB1*15 Common in MS patients. Probable in correlation with *04, [12,38,39]
*09, *12 alleles
Association with common MS
HLA‑DRB1*1602 Higher frequency in anti‑AQP4 positive patients in Han [40,41]
Chinese
Risk factor only for anti‑AQP4 positive NMO/NMOSD
HLA‑DP HLA‑DPB1*0501 Strong positive association with OSMS [12,38,40‑46]
Associated with opticospinal MS
Increased frequency in anti‑AQP4 positive patients
Risk factor only for anti‑AQP4 positive NMO/NMOSD patients
Susceptibility in anti‑AQP4 positive NMO in Han Chinese
Important role in the development of MS in general, but not
in OSMS. The strong association of DPB1*0501 with OSMS
may be due to the over‑representation of the DPB1*0301
allele among individuals in the non‑OSMS
HLA‑DPB1*0301 The most strongly associated allele with conventional MS, [38,44]
complete lack in OSMS
Possible protection against the development of OSMS
Brazilians HLA‑class I No data No data
HLA‑DR HLA‑DRB1*01 High frequency in NMO [56]
HLA‑DRB1*03 High frequency in NMO [56]
HLA‑DRB1*15 Low frequency in NMO, possible protective role [56]
African‑Americans HLA class I No data No data
and Afro‑Caribbeans HLA‑DR HLA‑DRB1*1501 None OSMS African‑American patient [57,58]
HLA‑DRB1*03 Highly noticed in NMO Afro‑Caribbean patients
HLA: human leukocyte antigens; NMO: neuromyelitis optica; IgG: immunoglobulin G; MS: multiple sclerosis; OSMS: opticospinal multiple sclerosis; AQP4: aquaporin‑4;
NMOSD: NMO‑spectrum diseases
in our consideration for a few years only, in contrast to REFERENCES
the 30 years of worldwide research regarding MS and
HLA. We expect this to be the new field of extensive 1. Katsavos S, Anagnostouli M. Biomarkers in multiple sclerosis: an
future research, in correlation with the accumulated up-to-date overview. Mult Scler Int 2013;2013:340508.
knowledge on the pathogenesis of NMO. 2. Ramagopalan SV, Maugeri NJ, Handunnetthi L, Lincoln MR,
Orton SM, Dyment DA, Deluca GC, Herrera BM, Chao MJ,
Sadovnick AD, Ebers GC, Knight JC. Expression of the multiple
Finally, the HLA profile in a patient with a CNS sclerosis-associated MHC class II Allele HLA-DRB1*1501 is
demyelinating disease tends to highlight different regulated by vitamin D. PLoS Genet 2009;5:e1000369.
backgrounds in immunopathogenesis and clinical 3. Anagnostouli M, Anagnostoulis G, Katsavos S, Panagiotou M,
phenotype, components which are very important in Kararizou E, Davaki P. HLA-DRB1 15:01 and Epstein-Barr virus
in a multiple sclerosis patient with psoriasis, nasopharyngeal and
the diagnosis and disease therapeutic decision making, breast cancers. Lessons for possible hidden links for autoimmunity
which is strongly requested. To this direction and in and cancer. J Neurol Sci 2014;339:26-31.
order to use HLA alleles, as a biomarker, in patients’ 4. Kikuchi S, Fukazawa T, Niino M, Yabe I, Miyagishi R, Hamada T,
early stratification, more HLA-genotyping studies are Tashiro K. Estrogen receptor gene polymorphism and multiple
needed, in different ethnic groups, in order to clarify, sclerosis in Japanese patients: interaction with HLA-DRB1*1501
and disease modulation. J Neuroimmunol 2002;128:77-81.
replicate or even expand the already existed results. 5. Cree BA, Goodin DS, Hauser SL. Neuromyelitis optica. Semin
48 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 2 | September 2014