Page 33 - Read Online
P. 33
the occurrence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, Burkitt having infectious mononucleosis syndrome and MS
lymphoma, Hodgkin disease, and immunoblastic show that MS often occurs in populations with high
lymphoma. Children infected with EBV often display EBV genetic susceptibility. Serum epidemiological
invisible symptoms. Adolescents and adults with and immunological evidence also suggests that the
EBV infection frequently suffer from infectious probability of occurrence in MS patients with EBV
mononucleosis syndrome. In addition, EBV infection antigen-antibody-positive serum is significantly higher
may correlate with the occurrence of some autoimmune than in the serum antibody-negative population.
[5]
diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematous [12] or EBV-CA and EBNA antibody titer has also been associated
MS. Epidemiological investigations with patients with the prevalence of MS. Although previous studies
[6]
[4]
using ELISA have confirmed the relationship between
serum/CSF EBV antigen-antibody and MS, this assay
fails to distinguish the EBV infection subtype. As a
result of ELISA’s poor reproducibility and the specificity
of the antigen preparation and complexity, we used
IFA in this experiment owing to IFA having merit
with a conjugate-standardized preparation and in
EBV-infection type differentiation. [7,8]
The IFA assay was used in 20 MS and 20 OND patients to
detect the CSF antibodies of anti-EBNA IgG, anti-EBV-CA
IgG, anti-EBV-CA IgG antibody affinity, anti-EBV-CA
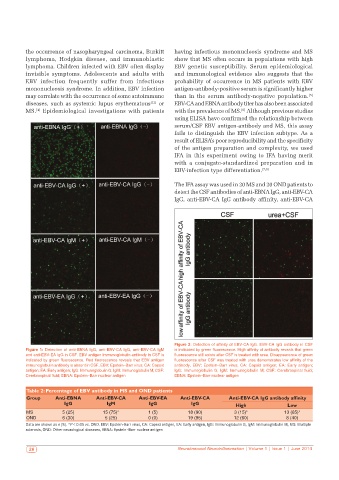
Figure 2: Detection of affinity of EBV-CA IgG. EBV-CA IgG antibody in CSF
Figure 1: Detection of anti-EBNA IgG, anti-EBV-CA IgG, anti-EBV-CA IgM is indicated by green fluorescence. High affinity of antibody reveals that green
and anti-EBV-EA IgG in CSF. EBV antigen immunoglobulin antibody in CSF is fluorescence still exists after CSF is treated with urea. Disappearance of green
indicated by green fluorescence. Red fluorescence reveals that EBV antigen fluorescence after CSF was treated with urea demonstrates low affinity of the
immunoglobulin antibody is absent in CSF. EBV: Epstein–Barr virus; CA: Capsid antibody. EBV: Epstein–Barr virus; CA: Capsid antigen; EA: Early antigen;
antigen; EA: Early antigen; IgG: Immunoglobulin G; IgM: Immunoglobulin M; CSF: IgG: Immunoglobulin G; IgM: Immunoglobulin M; CSF: Cerebrospinal fluid;
Cerebrospinal fluid; EBNA: Epstein–Barr nuclear antigen EBNA: Epstein–Barr nuclear antigen
Table 2: Percentage of EBV antibody in MS and OND patients
Group Anti‑EBNA Anti‑EBV‑CA Anti‑EBV‑EA Anti‑EBV‑CA Anti‑EBV‑CA IgG antibody affinity
IgG IgM IgG IgG High Low
MS 5 (25) 15 (75)* 1 (5) 18 (90) 3 (15)* 13 (65)*
OND 6 (30) 5 (25) 0 (0) 19 (95) 12 (60) 8 (40)
Data are shown as n (%). *P < 0.05 vs. OND. EBV: Epstein-Barr virus, CA: Capsid antigen, EA: Early antigen, IgG: Immunoglobulin G, IgM: Immunoglobulin M, MS: Multiple
sclerosis, OND: Other neurological diseases, EBNA: Epstein–Barr nuclear antigen
26 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 1 | June 2014