Page 16 - Read Online
P. 16
distinguished from CNS sarcoidosis, which leads to a lobes and frontal lobes, and makes the patient prone
significant increase in angiotensin-converting enzyme to epilepsy and mental symptoms. Herpes simplex
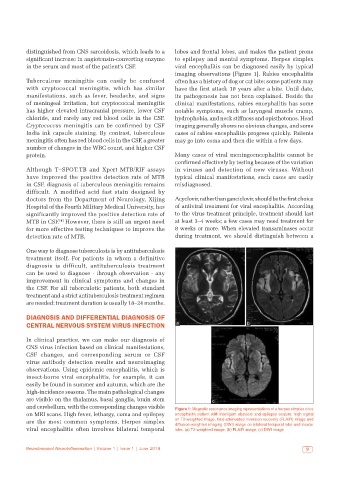
in the serum and most of the patient’s CSF. viral encephalitis can be diagnosed easily by typical
imaging observations [Figure 1]. Rabies encephalitis
Tuberculous meningitis can easily be confused often has a history of dog or cat bite; some patients may
with cryptococcal meningitis, which has similar have the first attack 10 years after a bite. Until date,
manifestations, such as fever, headache, and signs its pathogenesis has not been explained. Beside the
of meningeal irritation, but cryptococcal meningitis clinical manifestations, rabies encephalitis has some
has higher elevated intracranial pressure, lower CSF notable symptoms, such as laryngeal muscle cramp,
chloride, and rarely any red blood cells in the CSF. hydrophobia, and neck stiffness and opisthotonos. Head
Cryptococcus meningitis can be confirmed by CSF imaging generally shows no obvious changes, and some
India ink capsule staining. By contrast, tuberculous cases of rabies encephalitis progress quickly. Patients
meningitis often has red blood cells in the CSF, a greater may go into coma and then die within a few days.
number of changes in the WBC count, and higher CSF
protein. Many cases of viral meningoencephalitis cannot be
confirmed effectively by testing because of the variation
Although T-SPOT.TB and Xpert MTB/RIF assays in viruses and detection of new viruses. Without
have improved the positive detection rate of MTB typical clinical manifestations, such cases are easily
in CSF, diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis remains misdiagnosed.
difficult. A modified acid fast stain designed by
doctors from the Department of Neurology, Xijing Acyclovir, rather than ganciclovir, should be the first choice
Hospital of the Fourth Military Medical University, has of antiviral treatment for viral encephalitis. According
significantly improved the positive detection rate of to the virus treatment principle, treatment should last
[4]
MTB in CSF. However, there is still an urgent need at least 3–4 weeks; a few cases may need treatment for
for more effective testing techniques to improve the 8 weeks or more. When elevated transaminases occur
detection rate of MTB. during treatment, we should distinguish between a
One way to diagnose tuberculosis is by antituberculosis
treatment itself. For patients in whom a definitive
diagnosis is difficult, antituberculosis treatment
can be used to diagnose - through observation - any
improvement in clinical symptoms and changes in
the CSF. For all tuberculotic patients, both standard
treatment and a strict antituberculosis treatment regimen
are needed; treatment duration is usually 18–24 months.
DIAGNOSIS AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM VIRUS INFECTION a b
In clinical practice, we can make our diagnosis of
CNS virus infection based on clinical manifestations,
CSF changes, and corresponding serum or CSF
virus antibody detection results and neuroimaging
observations. Using epidemic encephalitis, which is
insect-borne viral encephalitis, for example, it can
easily be found in summer and autumn, which are the
high-incidence seasons. The main pathological changes
are visible on the thalamus, basal ganglia, brain stem c
and cerebellum, with the corresponding changes visible Figure 1: Magnetic resonance imaging representations of a herpes simplex virus
on MRI scans. High fever, lethargy, coma and epilepsy encephalitis patient with intelligent obstacle and epilepsy seizure: high signal
are the most common symptoms. Herpes simplex on T2-weighted image, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) image and
diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) image on bilateral temporal lobe and insular
viral encephalitis often involves bilateral temporal lobe. (a) T2-weighted image; (b) FLAIR image; (c) DWI image
Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 1 | June 2014 9