Page 36 - Read Online
P. 36
Min et al. Metab Target Organ Damage 2023;3:6 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/mtod.2023.09 Page 7 of 10
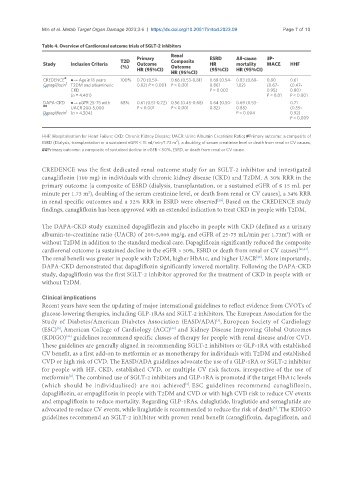
Table 4. Overview of Cardiorenal outcome trials of SGLT-2 inhibitors
Renal
Primary ESRD All-cause 3P-
Study Inclusion Criteria T2D Outcome Composite HR mortality MACE HHF
Outcome
(%)
HR (95%CI) (95%CI) HR (95%CI)
HR (95%CI)
#
CREDENCE ●→ Age ≥ 18 years 100% 0.70 (0.59- 0.66 (0.53-0.81) 0.68 (0.54- 0.83 (0.68- 0.80 0.61
Canagliflozin [ T2DM and albuminuric 0.82) P < 0.001 P < 0.001 0.86) 1.02) (0.67- (0.47-
29]
CKD P = 0.002 0.95) 0.80)
(n = 4,401) P = 0.01 P < 0.001
DAPA-CKD ●→ eGFR 25-75 with 68% 0.61 (0.51-0.72) 0.56 (0.45-0.68) 0.64 (0.50- 0.69 (0.53- 0.71
##
UACR 200-5,000 P < 0.001 P < 0.001 0.82) 0.88) (0.55-
[
Dapagliflozin (n = 4,304) P = 0.004 0.92)
30]
P = 0.009
HHF: Hospitalisation for Heart Failure; CKD: Chronic Kidney Disease; UACR: Urine Albumin Creatinine Ratio; #Primary outcome: a composite of
2
ESRD (Dialysis, transplantation or a sustained eGFR < 15 ml/min/1.73 m ), a doubling of serum creatinine level or death from renal or CV causes;
##Primary outcome: a composite of sustained decline in eGFR < 50%, ESRD, or death from renal or CV cause.
CREDENCE was the first dedicated renal outcome study for an SGLT-2 inhibitor and investigated
canagliflozin (100 mg) in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and T2DM. A 30% RRR in the
primary outcome [a composite of ESRD (dialysis, transplantation, or a sustained eGFR of ≤ 15 mL per
minute per 1.73 m ), doubling of the serum creatinine level, or death from renal or CV causes], a 34% RRR
2
[29]
in renal specific outcomes and a 32% RRR in ESRD were observed . Based on the CREDENCE study
findings, canagliflozin has been approved with an extended indication to treat CKD in people with T2DM.
The DAPA-CKD study examined dapagliflozin and placebo in people with CKD (defined as a urinary
albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) of 200-5,000 mg/g, and eGFR of 25-75 mL/min per 1.73m ) with or
2
without T2DM in addition to the standard medical care. Dapagliflozin significantly reduced the composite
cardiorenal outcome (a sustained decline in the eGFR > 50%, ESRD or death from renal or CV causes) [30,31] .
The renal benefit was greater in people with T2DM, higher HbA1c, and higher UACR . More importantly,
[30]
DAPA-CKD demonstrated that dapagliflozin significantly lowered mortality. Following the DAPA-CKD
study, dapagliflozin was the first SGLT-2 inhibitor approved for the treatment of CKD in people with or
without T2DM.
Clinical implications
Recent years have seen the updating of major international guidelines to reflect evidence from CVOTs of
glucose-lowering therapies, including GLP-1RAs and SGLT-2 inhibitors. The European Association for the
[3]
Study of Diabetes/American Diabetes Association (EASD/ADA) , European Society of Cardiology
(ESC) , American College of Cardiology (ACC) and Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes
[32]
[5]
(KDIGO) guidelines recommend specific classes of therapy for people with renal disease and/or CVD.
[33]
These guidelines are generally aligned in recommending SGLT-2 inhibitors or GLP-1RA with established
CV benefit, as a first add-on to metformin or as monotherapy for individuals with T2DM and established
CVD or high risk of CVD. The EASD/ADA guidelines advocate the use of a GLP-1RA or SGLT-2 inhibitor
for people with HF, CKD, established CVD, or multiple CV risk factors, irrespective of the use of
metformin . The combined use of SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1RA is promoted if the target HbA1c levels
[3]
(which should be individualised) are not achieved . ESC guidelines recommend canagliflozin,
[3]
dapagliflozin, or empagliflozin in people with T2DM and CVD or with high CVD risk to reduce CV events
and empagliflozin to reduce mortality. Regarding GLP-1RAs, dulaglutide, liraglutide and semaglutide are
[5]
advocated to reduce CV events, while liraglutide is recommended to reduce the risk of death . The KDIGO
guidelines recommend an SGLT-2 inhibitor with proven renal benefit (canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and