Page 23 - Read Online
P. 23
Page 10 of 16 Lugli et al. Microbiome Res Rep 2023;2:15 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/mrr.2022.21
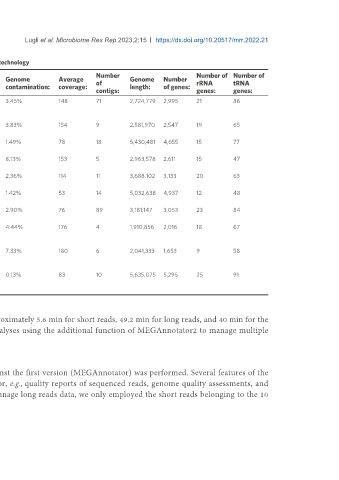
Table 2. MEGAnnotator2 report of 10 sequentially processed microbial genomes using long-read technology
High Number Number of Number of
Sequencing 16S rRNA gene Genome Genome Average Genome Number
SRA quality ANI screening: of rRNA tRNA
output: identity: completeness: contamination: coverage: length: of genes:
reads: contigs: genes: genes:
SRR12201911 500000 59283 Leuconostoc suionicum Leuconostoc 98.41% 3.45% 148 71 2,724,779 2,995 21 86
99.4% mesenteroides
96.7%
SRR13648750 500000 47731 Lactococcus lactis Lactococcus lactis 100% 3.83% 154 9 2,581,970 2,547 19 65
99.9% 88.1%
SRR15521836 500000 127174 Bacteroides salyersiae Bacteroides 97.63% 1.49% 78 18 5,430,481 4,655 15 77
99.9% salyersiae 99.0%
SRR17126341 500000 48110 Eubacterium eligens Eubacterium 98.25% 8.13% 153 5 2,963,578 2,611 15 47
100% eligens 100%
SRR17126949 500000 49224 Prevotella copri 99.8% Prevotella copri 97.97% 2.36% 114 11 3,688,102 3,133 20 63
100%
SRR17873544 500000 86673 Clostridium innocuum Clostridium 100% 1.42% 53 14 5,032,638 4,937 12 48
99.9% innocuum 97.1%
SRR17873548 500000 119899 Enterococcus hirae Enterococcus hirae 96.16% 2.90% 76 89 3,181,147 3,053 23 84
99.9% 98.9%
SRR21075862 500000 45558 Streptococcus Streptococcus 99.89% 4.44% 176 4 1,910,856 2,016 18 67
salivarius subsp. thermophilus
thermophilus 99.9% 99.2%
SRR21276823 500000 49609 Bifidobacterium Bifidobacterium 100% 7.33% 180 6 2,041,333 1,653 9 58
animalis subsp. lactis animalis 95.7%
100%
SRR22159808 500000 49946 Klebsiella pneumoniae Klebsiella 99.40% 0.13% 83 10 5,635,075 5,295 25 91
100% pneumoniae
99.0%
data. If the user is not interested in statistics, essential functions will take approximately 5.6 min for short reads, 49.2 min for long reads, and 40 min for the
usage of hybrid reads. Furthermore, no additional time is spent between analyses using the additional function of MEGAnnotator2 to manage multiple
samples.
MEGAnnotator2 improvement with respect to the old version
To highlight the enhancement made in MEGAnnotator2, a comparison against the first version (MEGAnnotator) was performed. Several features of the
updated pipeline were not compared due to their absence in MEGAnnotator, e.g., quality reports of sequenced reads, genome quality assessments, and
metabolic profiling. Furthermore, since the older pipeline version cannot manage long reads data, we only employed the short reads belonging to the 10