Page 20 - Read Online
P. 20
Lugli et al. Microbiome Res Rep 2023;2:15 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/mrr.2022.21 Page 9 of 16
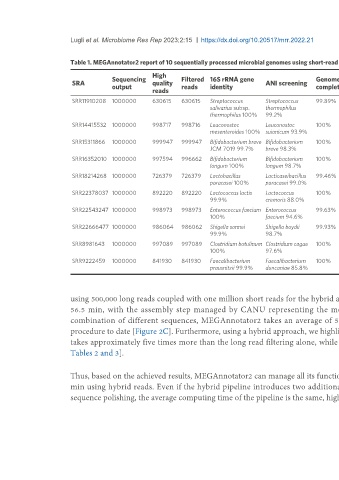
Table 1. MEGAnnotator2 report of 10 sequentially processed microbial genomes using short-read technology
High Number Number Number
Sequencing Filtered 16S rRNA gene Genome Genome Average Genome Number
SRA quality ANI screening of of rRNA of tRNA
output reads identity completeness contamination coverage length of genes
reads contigs genes genes
SRR11910208 1000000 630615 630615 Streptococcus Streptococcus 99.89% 11.19% 51 913 2,904,834 2,934 7 50
salivarius subsp. thermophilus
thermophilus 100% 99.2%
SRR14415532 1000000 998717 998716 Leuconostoc Leuconostoc 100% 0.18% 154 13 2,110,850 2,089 5 55
mesenteroides 100% suionicum 93.9%
SRR15311866 1000000 999947 999947 Bifidobacterium breve Bifidobacterium 100% 0.12% 126 35 2,374,842 2,011 3 55
JCM 7019 99.7% breve 98.3%
SRR16352010 1000000 997594 996662 Bifidobacterium Bifidobacterium 100% 0% 254 17 2,365,405 1,959 3 57
longum 100% longum 98.7%
SRR18214268 1000000 726379 726379 Lactobacillus Lacticaseibacillus 99.46% 0% 67 90 3,055,144 2,903 5 54
paracasei 100% paracasei 99.0%
SRR22378037 1000000 892220 892220 Lactococcus lactis Lactococcus 100% 0% 72 63 2,460,545 2,462 4 58
99.9% cremoris 88.0%
SRR22543247 1000000 998973 998973 Enterococcus faecium Enterococcus 99.63% 0.50% 104 147 3,1005,07 3,022 8 59
100% faecium 94.6%
SRR22666477 1000000 986064 986062 Shigella sonnei Shigella boydii 99.93% 0.33% 58 76 5,089,127 4,834 9 86
99.9% 98.7%
SRR8981643 1000000 997089 997089 Clostridium botulinum Clostridium cagae 100% 0% 140 47 3,825,030 3,529 14 77
100% 97.6%
SRR9222459 1000000 841930 841930 Faecalibacterium Faecalibacterium 100% 0.14% 72 87 3,356,538 3,213 9 63
prausnitzii 99.9% duncaniae 85.8%
using 500,000 long reads coupled with one million short reads for the hybrid approach. The average execution of the complete pipeline using long reads was
56.5 min, with the assembly step managed by CANU representing the most time-consuming (median of 2,761 sec) [Figure 2B]. Instead, by using a
combination of different sequences, MEGAnnotator2 takes an average of 53.5 min, validating the assembly step of long reads to be the most complex
procedure to date [Figure 2C]. Furthermore, using a hybrid approach, we highlighted the impact of long read filtering using the information of short reads that
takes approximately five times more than the long read filtering alone, while the polishing of the assembled data takes additional 3.4 min [Supplementary
Tables 2 and 3].
Thus, based on the achieved results, MEGAnnotator2 can manage all its functions in approximately 14.5 min for short reads, 56.5 min for long reads, and 53.5
min using hybrid reads. Even if the hybrid pipeline introduces two additional analyses represented by long-read filtering by short-read data and genome
sequence polishing, the average computing time of the pipeline is the same, highlighting high variability in the capability of the assembler to manage long reads