Page 65 - Read Online
P. 65
Page 8 of 11 Sawada et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2021;5:6 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.100
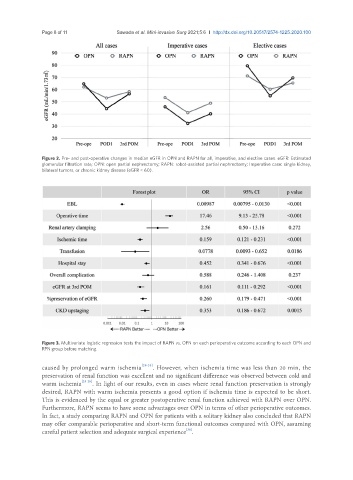
Figure 2. Pre- and post-operative changes in median eGFR in OPN and RAPN for all, imperative, and elective cases. eGFR: Estimated
glomerular filtration rate; OPN: open partial nephrectomy; RAPN: robot-assisted partial nephrectomy; Imperative case: single kidney,
bilateral tumors, or chronic kidney disease (eGFR < 60).
Figure 3. Multivariate logistic regression tests the impact of RAPN vs. OPN on each perioperative outcome according to each OPN and
RPN group before matching.
caused by prolonged warm ischemia [29-35] . However, when ischemia time was less than 20 min, the
preservation of renal function was excellent and no significant difference was observed between cold and
warm ischemia [25-28] . In light of our results, even in cases where renal function preservation is strongly
desired, RAPN with warm ischemia presents a good option if ischemia time is expected to be short.
This is evidenced by the equal or greater postoperative renal function achieved with RAPN over OPN.
Furthermore, RAPN seems to have some advantages over OPN in terms of other perioperative outcomes.
In fact, a study comparing RAPN and OPN for patients with a solitary kidney also concluded that RAPN
may offer comparable perioperative and short-term functional outcomes compared with OPN, assuming
[36]
careful patient selection and adequate surgical experience .