Page 220 - Read Online
P. 220
Page 4 of 6 Mok et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:26 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.04
A B
C D
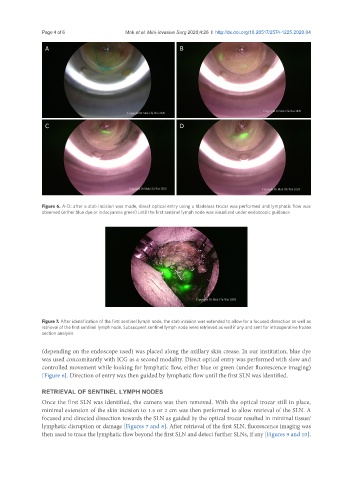
Figure 6. A-D: after a stab incision was made, direct optical entry using a bladeless trocar was performed and lymphatic flow was
observed (either blue dye or indocyanine green) until the first sentinel lymph node was visualized under endoscopic guidance
Figure 7. After identification of the first sentinel lymph node, the stab incision was extended to allow for a focused dissection as well as
retrieval of the first sentinel lymph node. Subsequent sentinel lymph node were retrieved as well if any and sent for intraoperative frozen
section analysis
(depending on the endoscope used) was placed along the axillary skin crease. In our institution, blue dye
was used concomitantly with ICG as a second modality. Direct optical entry was performed with slow and
controlled movement while looking for lymphatic flow, either blue or green (under fluorescence imaging)
[Figure 6]. Direction of entry was then guided by lymphatic flow until the first SLN was identified.
RETRIEVAL OF SENTINEL LYMPH NODES
Once the first SLN was identified, the camera was then removed. With the optical trocar still in place,
minimal extension of the skin incision to 1.5 or 2 cm was then performed to allow retrieval of the SLN. A
focused and directed dissection towards the SLN as guided by the optical trocar resulted in minimal tissue/
lymphatic disruption or damage [Figures 7 and 8]. After retrieval of the first SLN, fluorescence imaging was
then used to trace the lymphatic flow beyond the first SLN and detect further SLNs, if any [Figures 9 and 10].