Page 219 - Read Online
P. 219
Mok et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:26 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.04 Page 3 of 6
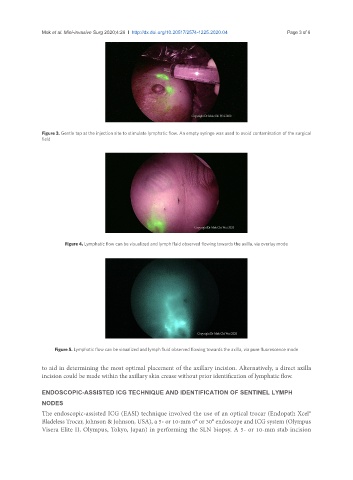
Figure 3. Gentle tap at the injection site to stimulate lymphatic flow. An empty syringe was used to avoid contamination of the surgical
field
Figure 4. Lymphatic flow can be visualized and lymph fluid observed flowing towards the axilla, via overlay mode
Figure 5. Lymphatic flow can be visualized and lymph fluid observed flowing towards the axilla, via pure fluorescence mode
to aid in determining the most optimal placement of the axillary incision. Alternatively, a direct axilla
incision could be made within the axillary skin crease without prior identification of lymphatic flow.
ENDOSCOPIC-ASSISTED ICG TECHNIQUE AND IDENTIFICATION OF SENTINEL LYMPH
NODES
The endoscopic-assisted ICG (EASI) technique involved the use of an optical trocar (Endopath Xcel®
Bladeless Trocar, Johnson & Johnson, USA), a 5- or 10-mm 0° or 30° endoscope and ICG system (Olympus
Visera Elite II, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) in performing the SLN biopsy. A 5- or 10-mm stab incision