Page 74 - Read Online
P. 74
Shimada et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2019;3:7 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2018.78 Page 7 of 11
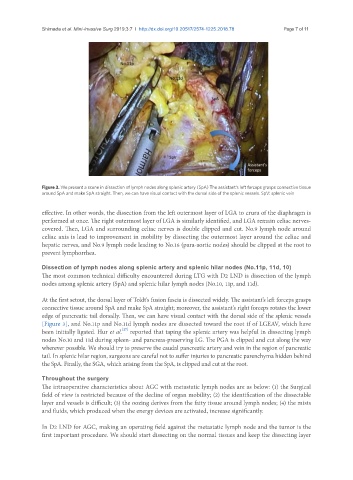
Figure 3. We present a scene in dissection of lymph nodes along splenic artery (SpA) The assistant’s left forceps grasps connective tissue
around SpA and make SpA straight. Then, we can have visual contact with the dorsal side of the splenic vessels. SpV: splenic vein
effective. In other words, the dissection from the left outermost layer of LGA to crura of the diaphragm is
performed at once. The right outermost layer of LGA is similarly identified, and LGA remain celiac nerves-
covered. Then, LGA and surrounding celiac nerves is double clipped and cut. No.9 lymph node around
celiac axis is lead to improvement in mobility by dissecting the outermost layer around the celiac and
hepatic nerves, and No.9 lymph node leading to No.16 (para-aortic nodes) should be clipped at the root to
prevent lymphorrhea.
Dissection of lymph nodes along splenic artery and splenic hilar nodes (No.11p, 11d, 10)
The most common technical difficulty encountered during LTG with D2 LND is dissection of the lymph
nodes among splenic artery (SpA) and splenic hilar lymph nodes (No.10, 11p, and 11d).
At the first setout, the dorsal layer of Toldt’s fusion fascia is dissected widely. The assistant’s left forceps grasps
connective tissue around SpA and make SpA straight; moreover, the assistant’s right forceps rotates the lower
edge of pancreatic tail dorsally. Then, we can have visual contact with the dorsal side of the splenic vessels
[Figure 3], and No.11p and No.11d lymph nodes are dissected toward the root if of LGEAV, which have
[27]
been initially ligated. Hur et al. reported that taping the splenic artery was helpful in dissecting lymph
nodes No.10 and 11d during spleen- and pancreas-preserving LG. The PGA is clipped and cut along the way
wherever possible. We should try to preserve the caudal pancreatic artery and vein in the region of pancreatic
tail. In splenic hilar region, surgeons are careful not to suffer injuries to pancreatic parenchyma hidden behind
the SpA. Finally, the SGA, which arising from the SpA, is clipped and cut at the root.
Throughout the surgery
The intraoperative characteristics about AGC with metastatic lymph nodes are as below: (1) the Surgical
field of view is restricted because of the decline of organ mobility; (2) the identification of the dissectable
layer and vessels is difficult; (3) the oozing derives from the fatty tissue around lymph nodes; (4) the mists
and fluids, which produced when the energy devices are activated, increase significantly.
In D2 LND for AGC, making an operating field against the metastatic lymph node and the tumor is the
first important procedure. We should start dissecting on the normal tissues and keep the dissecting layer