Page 35 - Read Online
P. 35
Mokhtar et al. Laparoscopic rectosigmoidopexy for intractable rectal prolapse in children
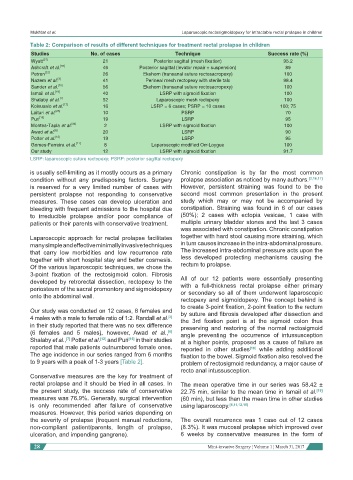
Table 2: Comparison of results of different techniques for treatment rectal prolapse in children
Studies No. of cases Technique Success rate (%)
Wyatt [21] 21 Posterior sagittal (mesh fixation) 95.2
Ashcraft et al. [18] 46 Posterior sagittal (levator repair + suspension) 89
Petren [22] 26 Ekehorn (transanal suture rectosacropexy) 100
Nazem et al. [3] 41 Perineal mesh rectopexy with sterile talc 98.4
Sander et al. [10] 56 Ekehorn (transanal suture rectosacropexy) 100
Ismail et al. [19] 40 LSRP with sigmoid fixation 100
Shalaby et al. [7] 52 Laparoscopic mesh rectopexy 100
Koivusalo et al. [17] 16 LSRP = 6 cases; PSRP = 10 cases 100; 75
Laituri et al. [23] 10 PSRP 70
Puri [15] 19 LSRP 95
Montes-Tapia et al. [24] 2 LSRP with sigmoid fixation 100
Awad et al. [6] 20 LSRP 90
Potter et al. [12] 19 LSRP 95
Gomes-Ferreira et al. [11] 8 Laparoscopic modified Orr-Loygue 100
Our study 12 LSRP with sigmoid fixation 91.7
LSRP: laparoscopic suture rectopexy; PSRP: posterior sagittal rectopexy
is usually self-limiting as it mostly occurs as a primary Chronic constipation is by far the most common
condition without any predisposing factors. Surgery prolapse association as noticed by many authors. [2,16,17]
is reserved for a very limited number of cases with However, persistent straining was found to be the
persistent prolapse not responding to conservative second most common presentation in the present
measures. These cases can develop ulceration and study which may or may not be accompanied by
bleeding with frequent admissions to the hospital due constipation. Straining was found in 6 of our cases
to irreducible prolapse and/or poor compliance of (50%); 2 cases with ectopia vesicae, 1 case with
patients or their parents with conservative treatment. multiple urinary bladder stones and the last 3 cases
was associated with constipation. Chronic constipation
Laparoscopic approach for rectal prolapse facilitates together with hard stool causing more straining, which
many simple and effective minimally invasive techniques in turn causes increase in the intra-abdominal pressure.
that carry low morbidities and low recurrence rate The increased intra-abdominal pressure acts upon the
together with short hospital stay and better cosmesis. less developed protecting mechanisms causing the
Of the various laparoscopic techniques, we chose the rectum to prolapse.
3-point fixation of the rectosigmoid colon. Fibrosis
developed by retrorectal dissection, rectopexy to the All of our 12 patients were essentially presenting
periosteum of the sacral promontory and sigmoidopexy with a full-thickness rectal prolapse either primary
or secondary so all of them underwent laparoscopic
onto the abdominal wall.
rectopexy and sigmoidopexy. The concept behind is
to create 3-point fixation, 2-point fixation to the rectum
Our study was conducted on 12 cases, 8 females and by suture and fibrosis developed after dissection and
4 males with a male to female ratio of 1:2. Randall et al. [2] the 3rd fixation point is at the sigmoid colon thus
in their study reported that there was no sex difference preserving and restoring of the normal rectosigmoid
(6 females and 5 males), however, Awad et al., angle preventing the occurrence of intussusception
[6]
Shalaby et al., Potter et al. [12] and Puri [15] in their studies at a higher points, proposed as a cause of failure as
[7]
reported that male patients outnumbered female ones. reported in other studies [18] while adding additional
The age incidence in our series ranged from 6 months fixation to the bowel. Sigmoid fixation also resolved the
to 9 years with a peak of 1-3 years [Table 2]. problem of rectosigmoid redundancy, a major cause of
recto anal intussusception.
Conservative measures are the key for treatment of
rectal prolapse and it should be tried in all cases. In The mean operative time in our series was 58.42 ±
the present study, the success rate of conservative 22.75 min, similar to the mean time in Ismail et al. [19]
measures was 76.9%. Generally, surgical intervention (60 min), but less than the mean time in other studies
is only recommended after failure of conservative using laparoscopy. [6,11,12,15]
measures. However, this period varies depending on
the severity of prolapse (frequent manual reductions, The overall recurrence was 1 case out of 12 cases
non-compliant patient/parents, length of prolapse, (8.3%). It was mucosal prolapse which improved over
ulceration, and impending gangrene). 6 weeks by conservative measures in the form of
28 Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ March 31, 2017