Page 22 - Read Online
P. 22
Sawabata et al. Pulmonary wedge resection for NSCLC
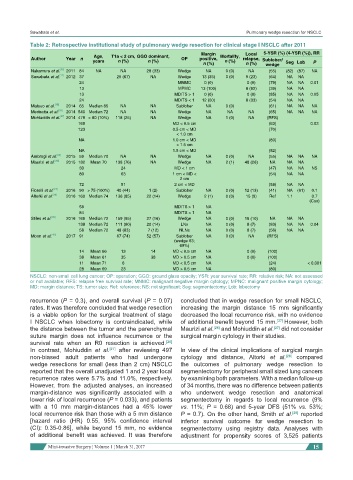
Table 2: Retrospective institutional study of pulmonary wedge resection for clinical stage I NSCLC after 2011
Margin Local 5-YSR (%) {4-YSR (%)}, RR
Age, T1a < 2 cm, GGO dominant, Mortality,
Author Year n OP positive, relapse, Sublober/
years n (%) n (%) n (%) Seg Lob P
n (%) n (%) wedge
Nakamura et al. [16] 2011 84 NA NA 28 (33) Wedge NA 0 (0) NA (55) (82) (87) NA
Sawabata et al. [17] 2012 37 25 (67) NA Wedge 13 (35) 0 (0) 9 (23) (64) NA NA
24 MNMC 0 (0) 0 (0) (79) NA NA 0.01
13 MPMC 13 (100) 8 (62) (39) NA NA
13 MD/TS > 1 0 (0) 0 (0) (85) NA NA 0.05
24 MD/TS < 1 12 (50) 8 (33) (54) NA NA
Matsuo et al. [18] 2014 65 Median 65 NA NA Sublober NA 0 (0) (61) NA NA NA
Mediratta et al. [19] 2014 540 Median 72 NA NA Wedge NA NA NA (65) NA NA NA
Mohiuddin et al. [27] 2014 479 > 80 (10%) 118 (25) NA Wedge NA 1 (0) NA (RFS)
169 MD < 0.5 cm {63} 0.03
123 0.5 cm < MD {70}
< 1.0 cm
NA 1.0 cm < MD {80}
< 1.5 cm
NA 1.5 cm < MD {82}
Ambrogi et al. [20] 2015 59 Median 70 NA NA Wedge NA 0 (0) NA (55) NA NA NA
Maurizi et al. [26] 2015 182 Mean 70 138 (76) NA Wedge NA 2 (1) 48 (26) NA NA NA
30 24 MD < 1 cm (47) NA NA NS
80 63 1 cm < MD < (54) NA NA
2 cm
72 51 2 cm < MD (58) NA NA
Fiorelli et al. [21] 2016 90 > 75 (100%) 40 (44) 1 (2) Sublober NA 0 (0) 12 (13) (41) NA (61) 0.1
Altorki et al. [28] 2016 160 Median 74 136 (85) 22 (14) Wedge 2 (1) 0 (0) 15 (9) Ref 1.1 0.7
(Cox)
58 MD/TS > 1 NA
84 MD/TS < 1 NA
Stiles et al. [36] 2016 166 Median 72 159 (95) 27 (16) Wedge NA 0 (0) 16 (10) NA NA NA
138 Median 72 111 (80) 20 (14) LNs NA 0 (0) 8 (7) (83) NA NA 0.04
58 Median 72 48 (83) 7 (12) NLNs NA 0 (0) 8 (7) (56) NA NA
Moon et al. [41] 2017 91 67 (74) 52 (57) Sublober NA 0 (0) NA (RFS)
(wedge 63;
69%)
14 Mean 66 13 14 MD < 0.5 cm NA 0 (0) (100)
38 Mean 61 35 38 MD > 0.5 cm NA 0 (0) (100)
11 Mean 71 6 MD < 0.5 cm NA (24) < 0.001
28 Mean 69 23 MD > 0.5 cm NA (80)
NSCLC: non-small cell lung cancer; OP: operation; GGO: ground glass opacity; YSR: year survival rate; RR: relative risk; NA: not assessed
or not available; RFS: relapse free survival rate; MNMC: malignant negative margin cytology; MPNC: malignant positive margin cytology;
MD: margin distance; TS: tumor size; Ref: reference; NS: not significant; Seg: segmentectomy; Lob: lobectomy
recurrence (P = 0.3), and overall survival (P = 0.07) concluded that in wedge resection for small NSCLC,
rates. It was therefore concluded that wedge resection increasing the margin distance 15 mm significantly
is a viable option for the surgical treatment of stage decreased the local recurrence risk, with no evidence
I NSCLC when lobectomy is contraindicated, while of additional benefit beyond 15 mm. [27] However, both
the distance between the tumor and the parenchymal Maurizi et al. [26] and Mohiuddin et al. [27] did not consider
suture margin does not influence recurrence or the surgical margin cytology in their studies.
survival rate when an R0 resection is achieved. [26]
In contrast, Mohiuddin et al. [27] after reviewing 497 In view of the clinical implications of surgical margin
non-biased adult patients who had undergone cytology and distance, Altorki et al. [28] compared
wedge resections for small (less than 2 cm) NSCLC the outcomes of pulmonary wedge resection to
reported that the overall unadjusted 1 and 2 year local segmentectomy for peripheral small sized lung cancers
recurrence rates were 5.7% and 11.0%, respectively. by examining both parameters. With a median follow-up
However, from the adjusted analyses, an increased of 34 months, there was no difference between patients
margin-distance was significantly associated with a who underwent wedge resection and anatomical
lower risk of local recurrence (P = 0.033), and patients segmentectomy in regards to local recurrence (9%
with a 10 mm margin-distances had a 45% lower vs. 11%; P = 0.68) and 5-year DFS (51% vs. 53%;
local recurrence risk than those with a 5 mm distance P = 0.7). On the other hand, Smith et al. [29] reported
[hazard ratio (HR) 0.55, 95% confidence interval inferior survival outcome for wedge resection to
(CI): 0.35-0.86], while beyond 15 mm, no evidence segmentectomy using registry data. Analyses with
of additional benefit was achieved. It was therefore adjustment for propensity scores of 3,525 patients
Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ March 31, 2017 15