Page 21 - Read Online
P. 21
Sawabata et al. Pulmonary wedge resection for NSCLC
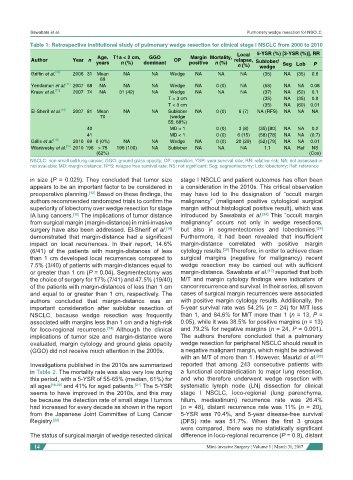
Table 1: Retrospective institutional study of pulmonary wedge resection for clinical stage I NSCLC from 2000 to 2010
Age, T1a < 2 cm, GGO Margin Mortality, Local 5-YSR (%) [3-YSR (%)], RR
Author Year n years n (%) dominant OP positive n (%) relapse, Sublober/
n (%) wedge Seg Lob P
Griffin et al. [10] 2006 31 Mean NA NA Wedge NA NA NA (35) NA (35) 0.8
69
Yendamuri et al. [11] 2007 68 NA NA NA Wedge NA 0 (0) NA (58) NA NA 0.08
Kraev et al. [12] 2007 74 NA 31 (42) NA Wedge NA NA NA (37) NA (52) 0.1
T > 3 cm (35) NA (35) 0.9
T < 3 cm (35) NA (60) 0.01
El-Sherif et al. [14] 2007 81 Mean NA NA Sublober NA 0 (0) 6 (7) NA (RFS) NA NA NA
70 (wedge
55; 68%)
40 MD > 1 0 (0) 3 (8) (35) [80] NA NA 0.2
41 MD < 1 0 (0) 6 (15) (58) [78] NA NA (0.7)
Grills et al. [13] 2010 69 0 (0%) NA NA Wedge NA 0 (0) 20 (29) (52) [79] NA NA 0.01
Wisnivesky et al. [15] 2010 196 > 75 196 (100) NA Sublober NA NA NA 1.1 NA Ref NS
(62%) (Cox)
NSCLC: non-small cell lung cancer; GGO: ground glass opacity; OP: operation; YSR: year survival rate; RR: relative risk; NA: not assessed or
not available; MD: margin distance; RFS: relapse free survival rate; NS: not significant; Seg: segmentectomy; Lob: lobectomy; Ref: reference
in size (P = 0.029). They concluded that tumor size stage I NSCLC and patient outcomes has often been
appears to be an important factor to be considered in a consideration in the 2010s. This critical observation
preoperative planning. [12] Based on these findings, the may have led to the designation of “occult margin
authors recommended randomized trials to confirm the malignancy” (malignant positive cytological surgical
superiority of lobectomy over wedge resection for stage margin without histological positive result), which was
IA lung cancers. [12] The implications of tumor distance introduced by Sawabata et al. [23] This “occult margin
from surgical margin (margin-distance) in mini-invasive malignancy” occurs not only in wedge resections,
surgery have also been addressed. El-Sherif et al. [14] but also in segmentectomies and lobectomies. [24]
demonstrated that margin-distance had a significant Furthermore, it had been revealed that insufficient
impact on local recurrences. In their report, 14.6% margin-distance correlated with positive margin
(6/41) of the patients with margin-distances of less cytology results. [25] Therefore, in order to achieve clean
than 1 cm developed local recurrences compared to surgical margins (negative for malignancy) recent
7.5% (3/40) of patients with margin-distances equal to wedge resection may be carried out with sufficient
or greater than 1 cm (P = 0.04). Segmentectomy was margin-distance. Sawabata et al. [17] reported that both
the choice of surgery for 17% (7/41) and 47.5% (19/40) M/T and margin cytology findings were indicators of
of the patients with margin-distances of less than 1 cm cancer recurrence and survival. In their series, all seven
and equal to or greater than 1 cm, respectively. The cases of surgical margin recurrences were associated
authors concluded that margin-distance was an with positive margin cytology results. Additionally, the
important consideration after sublobar resection of 5-year survival rate was 54.2% (n = 24) for M/T less
NSCLC, because wedge resection was frequently than 1, and 84.6% for M/T more than 1 (n = 13, P =
associated with margins less than 1 cm and a high-risk 0.05), while it was 38.5% for positive margins (n = 13)
for loco-regional recurrence. [14] Although the clinical and 79.2% for negative margins (n = 24, P = 0.001).
implications of tumor size and margin-distance were The authors therefore concluded that a pulmonary
evaluated, margin cytology and ground glass opacity wedge resection for peripheral NSCLC should result in
(GGO) did not receive much attention in the 2000s. a negative malignant margin, which might be achieved
with an M/T of more than 1. However, Maurizi et al. [26]
Investigations published in the 2010s are summarized reported that among 243 consecutive patients with
in Table 2. The mortality rate was also very low during a functional contraindication to major lung resection,
this period, with a 5-YSR of 55-65% (median, 61%) for and who therefore underwent wedge resection with
all ages [16-20] and 41% for aged patients. [21] The 5-YSR systematic lymph node (LN) dissection for clinical
seems to have improved in the 2010s, and this may stage I NSCLC, loco-regional (lung parenchyma,
be because the detection rate of small stage I tumors hilum, mediastinum) recurrence rate was 26.4%
had increased for every decade as shown in the report (n = 48), distant recurrence rate was 11% (n = 20),
from the Japanese Joint Committee of Lung Cancer 5-YSR was 70.4%, and 5-year disease-free survival
Registry. [22] (DFS) rate was 51.7%. When the first 3 groups
were compared, there was no statistically significant
The status of surgical margin of wedge resected clinical difference in loco-regional recurrence (P = 0.9), distant
14 Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ March 31, 2017