Page 36 - Read Online
P. 36
Parra et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2024;8:16 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2024.01 Page 7 of 13
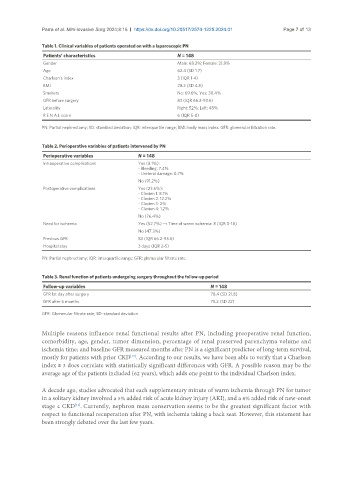
Table 1. Clinical variables of patients operated on with a laparoscopic PN
Patients’ characteristics N = 148
Gender Male: 68.2%; Female: 31.8%
Age 62.4 (SD 1.7)
Charlson’s index 3 (IQR 1-4)
BMI 28.2 (SD 4.8)
Smokers No: 69.6%; Yes: 30.4%
GFR before surgery 83 (IQR 66.2-93.6)
Laterality Right: 52%; Left: 48%
R.E.N.A.L score 6 (IQR 5-8)
PN: Partial nephrectomy; SD: standard deviation; IQR: interquartile range; BMI: body mass index. GFR: glomerular filtration rate.
Table 2. Perioperative variables of patients intervened by PN
Perioperative variables N = 148
Intraoperative complications Yes (8.1%):
- Bleeding: 7.4%
- Ureteral damage: 0.7%
No (91.2%)
Postoperative complications Yes (23.6%):
- Clavien 1: 8.1%
- Clavien 2: 12.2%
- Clavien 3: 2%
- Clavien 4: 1.2%
No (76.4%)
Need for ischemia Yes (52.7%) → Time of warm ischemia: 8 (IQR 0-18)
No (47.3%)
Previous GFR 83 (IQR 66.2-93.6)
Hospital stay 3 days (IQR 2-5)
PN: Partial nephrectomy; IQR: interquartile range; GFR: glomerular filtrate rate.
Table 3. Renal function of patients undergoing surgery throughout the follow-up period
Follow-up variables N = 148
GFR 1st day after surgery 78.4 (SD 21.8)
GFR after 6 months 75.2 (SD 22)
GFR: Glomerular filtrate rate; SD: standard deviation.
Multiple reasons influence renal functional results after PN, including preoperative renal function,
comorbidity, age, gender, tumor dimension, percentage of renal preserved parenchyma volume and
ischemia time; and baseline GFR measured months after PN is a significant predictor of long-term survival,
mostly for patients with prior CKD . According to our results, we have been able to verify that a Charlson
[10]
index ≥ 3 does correlate with statistically significant differences with GFR. A possible reason may be the
average age of the patients included (62 years), which adds one point to the individual Charlson index.
A decade ago, studies advocated that each supplementary minute of warm ischemia through PN for tumor
in a solitary kidney involved a 5% added risk of acute kidney injury (AKI), and a 6% added risk of new-onset
[11]
stage 4 CKD . Currently, nephron mass conservation seems to be the greatest significant factor with
respect to functional recuperation after PN, with ischemia taking a back seat. However, this statement has
been strongly debated over the last few years.