Page 27 - Read Online
P. 27
McBee et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2021;5:18 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2021.08 Page 5 of 6
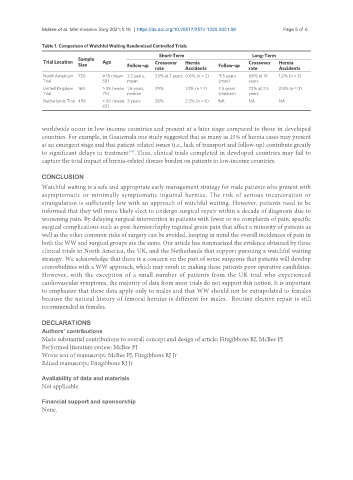
Table 1. Comparison of Watchful Waiting Randomized Controlled Trials
Short-Term Long-Term
Sample
Trial Location Age Crossover Hernia Crossover Hernia
Size Follow-up Follow-up
rate Accidents rate Accidents
North American 720 ≥ 18 (mean 3.2 years, 23% at 2 years 0.6% (n = 2) 11.5 years 68% at 10 1.2% (n = 3)
Trial 58) mean (max) years
United Kingdom 160 > 55 (mean 1.6 years, 29% 1.3% (n = 1) 7.5 years 72% at 7.5 2.5% (n = 2)
Trial 70) median (median) years
Netherlands Trial 496 > 50 (mean 3 years 38% 2.3% (n = 6) NA NA NA
65)
worldwide occur in low-income countries and present at a later stage compared to those in developed
countries. For example, in Guatemala one study suggested that as many as 25% of hernia cases may present
at an emergent stage and that patient-related issues (i.e., lack of transport and follow-up) contribute greatly
[16]
to significant delays in treatment . Thus, clinical trials completed in developed countries may fail to
capture the total impact of hernia-related disease burden on patients in low-income countries.
CONCLUSION
Watchful waiting is a safe and appropriate early management strategy for male patients who present with
asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic inguinal hernias. The risk of serious incarceration or
strangulation is sufficiently low with an approach of watchful waiting. However, patients need to be
informed that they will more likely elect to undergo surgical repair within a decade of diagnosis due to
worsening pain. By delaying surgical intervention in patients with fewer or no complaints of pain, specific
surgical complications such as post-herniorrhaphy inguinal groin pain that affect a minority of patients as
well as the other common risks of surgery can be avoided, keeping in mind the overall incidences of pain in
both the WW and surgical groups are the same. Our article has summarized the evidence obtained by three
clinical trials in North America, the UK, and the Netherlands that support pursuing a watchful waiting
strategy. We acknowledge that there is a concern on the part of some surgeons that patients will develop
comorbidities with a WW approach, which may result in making these patients poor operative candidates.
However, with the exception of a small number of patients from the UK trial who experienced
cardiovascular symptoms, the majority of data from most trials do not support this notion. It is important
to emphasize that these data apply only to males and that WW should not be extrapolated to females
because the natural history of femoral hernias is different for males. Routine elective repair is still
recommended in females.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Made substantial contributions to overall concept and design of article: Fitzgibbons RJ, McBee PJ
Performed literature review: McBee PJ
Wrote text of manuscript: McBee PJ, Fitzgibbons RJ Jr
Edited manuscript: Fitzgibbons RJ Jr
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Financial support and sponsorship
None.