Page 13 - Read Online
P. 13
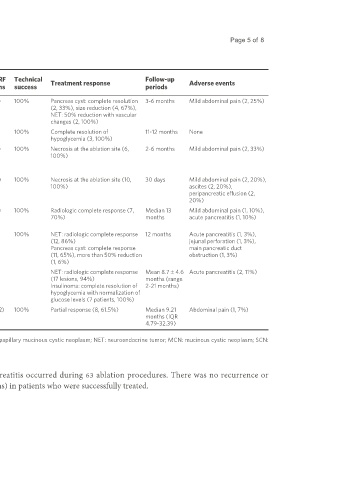
Cho et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2021;5:20 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2021.11 Page 5 of 8
Table 1. Summary of published data on EUS-RFA
Application
Indications and number RF Mean tumor Mean RF Technical Follow-up
Ref. (year) power and Treatment response Adverse events
of patients devices size (range) sessions success periods
time
[19]
Pai et al. Mucinous cyst (4), IPMN Habib EUS- Pancreas cyst: 5-25W, 90-120s 1.3 (1-2) 100% Pancreas cyst: complete resolution 3-6 months Mild abdominal pain (2, 25%)
(2015) (1), microcystic adenoma RFA 36.5 (24-70), (2, 33%), size reduction (4, 67%),
(1), NET (2) catheter NET: 27.5 (15- NET: 50% reduction with vascular
40) changes (2, 100%)
[7]
Lakhtakia et al. Insulinoma (3) EUSLA 19 (14-22) 50W, 10-15s 1 100% Complete resolution of 11-12 months None
(2016) hypoglycemia (3, 100%)
[8]
Song et al. Locally advanced EUSLA 38 (30-90) 20-50W, 10s 1.3 (1-2) 100% Necrosis at the ablation site (6, 2-6 months Mild abdominal pain (2, 33%)
(2016) pancreatic cancer (4), 100%)
metastatic pancreatic
cancer (2)
[9]
Scopelliti et al. Locally advanced EUSLA 49.2 (35-75) 20-30W, 100- 1.4 (1-2) 100% Necrosis at the ablation site (10, 30 days Mild abdominal pain (2, 20%),
(2018) pancreatic cancer (10) 560s 100%) ascites (2, 20%),
peripancreatic effusion (2,
20%)
[5]
Choi et al. NET (7), solid EUSLA 20 (8-28) 50W 1.6 (1-3) 100% Radiologic complete response (7, Median 13 Mild abdominal pain (1, 10%),
(2018) pseudopapillary neoplasm 70%) months acute pancreatitis (1, 10%)
(2), insulinoma (1)
[13]
Barthet et al. IPMN (16), MCN (1), NET EUSLA PCL: 28 (9-60), 50W NA 100% NET: radiologic complete response 12 months Acute pancreatitis (1, 3%),
(2019) (14 lesions in 12) NET: 13.1 (10- (12, 86%) jejunal perforation (1, 3%),
20) Pancreas cyst: complete response main pancreatic duct
(11, 65%), more than 50% reduction obstruction (1, 3%)
(1, 6%)
[14]
Oleinikov et al. NET (18 lesions in 11 EUSLA 14.3 (4.5-30) 10-50W, 5-12s NET: radiologic complete response Mean 8.7 ± 4.6 Acute pancreatitis (2, 11%)
(2019) patients), insulinoma (9 (17 lesions, 94%) months (range
lesions in 7 patients) Insulinoma: complete resolution of 2-21 months)
hypoglycemia with normalization of
glucose levels (7 patients, 100%)
[20]
Oh et al. Microcystic SCN (13) EUSLA 50 (34-52.5) 50W 1.46 (1-2) 100% Partial response (8, 61.5%) Median 9.21 Abdominal pain (1, 7%)
(2020) months (IQR
4.79-32.39)
EUS-RFA: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation; RF: radiofrequency; IPMN: intraductal papillary mucinous cystic neoplasm; NET: neuroendocrine tumor; MCN: mucinous cystic neoplasm; SCN:
serous cystic neoplasm; PCL: pancreatic cystic lesion; IQR: interquartile range.
45%) or 2 (24 tumors, 60%) sessions of EUS-ELA. Two cases (3.4%) of pancreatitis occurred during 63 ablation procedures. There was no recurrence or
progression during a median follow-up period of 42 months (IQR, 39-46 months) in patients who were successfully treated.