Page 25 - Read Online
P. 25
Ziogas et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:69 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.63 Page 5 of 11
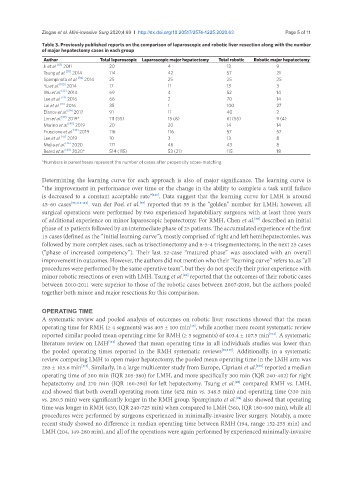
Table 3. Previously published reports on the comparison of laparoscopic and robotic liver resection along with the number
of major hepatectomy cases in each group
Author Total laparoscopic Laparoscopic major hepatectomy Total robotic Robotic major hepatectomy
Ji et al. [83] 2011 20 4 13 9
Tsung et al. [20] 2014 114 42 57 21
Spampinato et al. [94] 2014 25 25 25 25
Yu et al. [105] 2014 17 11 13 3
Wu et al. [22] 2014 69 4 52 14
Lee et al. [24] 2016 66 2 70 14
Lai et al. [26] 2016 35 1 100 27
Efanov et al. [34] 2017 91 11 40 2
Lim et al. [39] 2019* 111 (55) 15 (8) 61 (55) 9 (4)
Marino et al. [40] 2019 20 20 14 14
Fruscione et al. [42] 2019 116 116 57 57
Lee et al. [45] 2019 10 3 13 8
Mejia et al. [46] 2020 171 46 43 8
Beard et al. [48] 2020* 514 (115) 53 (21) 115 18
*Numbers in parentheses represent the number of cases after propensity score-matching
Determining the learning curve for each approach is also of major significance. The learning curve is
“the improvement in performance over time or the change in the ability to complete a task until failure
is decreased to a constant acceptable rate” . Data suggest that the learning curve for LMH is around
[110]
45-60 cases [93,111-113] . van der Poel et al. reported that 55 is the “golden” number for LMH; however, all
[93]
surgical operations were performed by two experienced hepatobiliary surgeons with at least three years
of additional experience on minor laparoscopic hepatectomy. For RMH, Chen et al. described an initial
[30]
phase of 15 patients followed by an intermediate phase of 25 patients. The accumulated experience of the first
15 cases (defined as the “initial learning curve”), mostly comprised of right and left hemihepatectomies, was
followed by more complex cases, such as trisectionectomy and 8-5-4 trisegmentectomy, in the next 25 cases
(“phase of increased competency”). Their last 52-case “matured phase” was associated with an overall
improvement in outcomes. However, the authors did not mention who their “learning curve” refers to, as “all
procedures were performed by the same operative team”, but they do not specify their prior experience with
minor robotic resections or even with LMH. Tsung et al. reported that the outcomes of their robotic cases
[20]
between 2010-2011 were superior to those of the robotic cases between 2007-2010, but the authors pooled
together both minor and major resections for this comparison.
OPERATING TIME
A systematic review and pooled analysis of outcomes on robotic liver resections showed that the mean
operating time for RMH (≥ 4 segments) was 405 ± 100 min , while another more recent systematic review
[18]
reported similar pooled mean operating rime for RMH (≥ 3 segments) of 403.4 ± 107.5 min . A systematic
[114]
literature review on LMH showed that mean operating time in all individuals studies was lower than
[115]
the pooled operating times reported in the RMH systematic reviews [18,114] . Additionally, in a systematic
review comparing LMH to open major hepatectomy, the pooled mean operating time in the LMH arm was
285 ± 105.6 min . Similarly, in a large multicenter study from Europe, Cipriani et al. reported a median
[116]
[109]
operating time of 300 min (IQR 205-380) for LMH, and more specifically 300 min (IQR 240-402) for right
hepatectomy and 270 min (IQR 160-290) for left hepatectomy. Tsung et al. compared RMH vs. LMH,
[20]
and showed that both overall operating room time (452 min vs. 348.5 min) and operating time (330 min
vs. 280.5 min) were significantly longer in the RMH group. Spampinato et al. also showed that operating
[94]
time was longer in RMH (430, IQR 240-725 min) when compared to LMH (360, IQR 180-600 min), while all
procedures were performed by surgeons experienced in minimally-invasive liver surgery. Notably, a more
recent study showed no difference in median operating time between RMH (194, range 152-255 min) and
LMH (204, 149-280 min), and all of the operations were again performed by experienced minimally-invasive