Page 38 - Read Online
P. 38
Page 12 of 20 Nwaiwu et al. Mini-invasive Surg. 2025;9:20 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2024.112
[37]
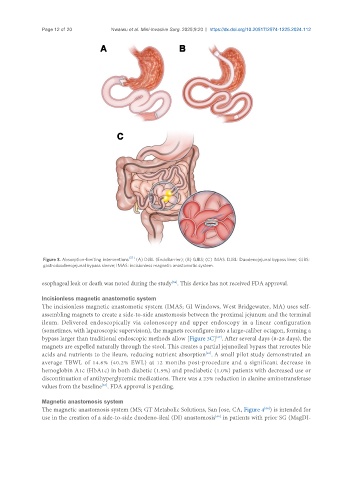
Figure 3. Absorption-limiting interventions . (A) DJBL (EndoBarrier); (B) GJBS; (C) IMAS. DJBL: Duodenojejunal bypass liner; GJBS:
gastroduodenojejunal bypass sleeve; IMAS: incisionless magnetic anastomotic system.
esophageal leak or death was noted during the study . This device has not received FDA approval.
[64]
Incisionless magnetic anastomotic system
The incisionless magnetic anastomotic system (IMAS; GI Windows, West Bridgewater, MA) uses self-
assembling magnets to create a side-to-side anastomosis between the proximal jejunum and the terminal
ileum. Delivered endoscopically via colonoscopy and upper endoscopy in a linear configuration
(sometimes, with laparoscopic supervision), the magnets reconfigure into a large-caliber octagon, forming a
bypass larger than traditional endoscopic methods allow [Figure 3C] . After several days (8-28 days), the
[37]
magnets are expelled naturally through the stool. This creates a partial jejunoileal bypass that reroutes bile
acids and nutrients to the ileum, reducing nutrient absorption . A small pilot study demonstrated an
[65]
average TBWL of 14.6% (40.2% EWL) at 12 months post-procedure and a significant decrease in
hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) in both diabetic (1.9%) and prediabetic (1.0%) patients with decreased use or
discontinuation of antihyperglycemic medications. There was a 23% reduction in alanine aminotransferase
values from the baseline . FDA approval is pending.
[65]
Magnetic anastomosis system
[66]
The magnetic anastomosis system (MS; GT Metabolic Solutions, San Jose, CA, Figure 4 ) is intended for
use in the creation of a side-to-side duodeno-ileal (DI) anastomosis in patients with prior SG (MagDI-
[66]