Page 196 - Read Online
P. 196
Page 6 of 12 Chen et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2018;2:43 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2018.42
A B
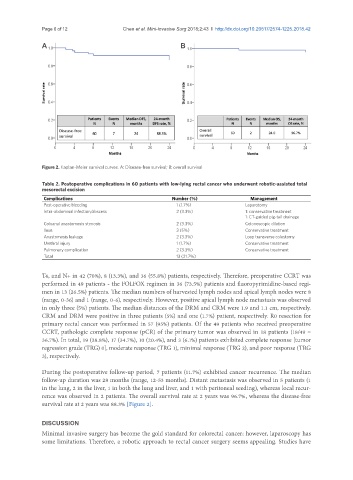
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier survival curves. A: Disease-free survival; B: overall survival
Table 2. Postoperative complications in 60 patients with low-lying rectal cancer who underwent robotic-assisted total
mesorectal excision
Complications Number (%) Management
Post-operative bleeding 1 (1.7%) Laparotomy
Intra-abdominal infection/abscess 2 (3.3%) 1: conservative treatment
1: CT-guided pig-tail drainage
Coloanal anastomosis stenosis 2 (3.3%) Colonoscopic dilation
Ileus 3 (5%) Conservative treatment
Anastomosis leakage 2 (3.3%) Loop transverse colostomy
Urethral injury 1 (1.7%) Conservative treatment
Pulmonary complication 2 (3.3%) Conservative treatment
Total 13 (21.7%)
T4, and N+ in 42 (70%), 8 (13.3%), and 36 (55.8%) patients, respectively. Therefore, preoperative CCRT was
performed in 49 patients - the FOLFOX regimen in 36 (73.5%) patients and fluoropyrimidine-based regi-
men in 13 (26.5%) patients. The median numbers of harvested lymph nodes and apical lymph nodes were 8
(range, 0-36) and 1 (range, 0-6), respectively. However, positive apical lymph node metastasis was observed
in only three (5%) patients. The median distances of the DRM and CRM were 1.9 and 1.1 cm, respectively.
CRM and DRM were positive in three patients (5%) and one (1.7%) patient, respectively. R0 resection for
primary rectal cancer was performed in 57 (95%) patients. Of the 49 patients who received preoperative
CCRT, pathologic complete response (pCR) of the primary tumor was observed in 18 patients (18/49 =
36.7%). In total, 19 (38.8%), 17 (34.7%), 10 (20.4%), and 3 (6.1%) patients exhibited complete response [tumor
regression grade (TRG) 0], moderate response (TRG 1), minimal response (TRG 2), and poor response (TRG
3), respectively.
During the postoperative follow-up period, 7 patients (11.7%) exhibited cancer recurrence. The median
follow-up duration was 28 months (range, 12-53 months). Distant metastasis was observed in 5 patients (1
in the lung, 2 in the liver, 1 in both the lung and liver, and 1 with peritoneal seeding), whereas local recur-
rence was observed in 2 patients. The overall survival rate at 2 years was 96.7%, whereas the disease-free
survival rate at 2 years was 88.3% [Figure 2].
DISCUSSION
Minimal invasive surgery has become the gold standard for colorectal cancer; however, laparoscopy has
some limitations. Therefore, a robotic approach to rectal cancer surgery seems appealing. Studies have