Page 19 - Read Online
P. 19
Page 10 of 11 Matto et al. Mini-invasive Surg. 2025;9:19 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2025.51
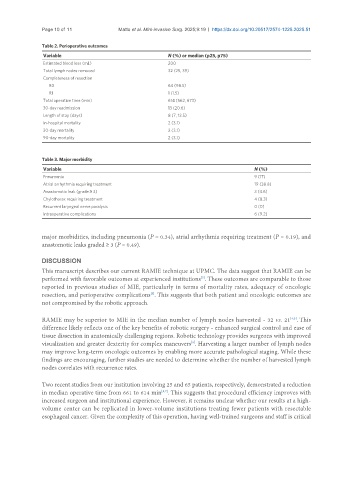
Table 2. Perioperative outcomes
Variable N (%) or median (p25, p75)
Estimated blood loss (mL) 200
Total lymph nodes removed 32 (25, 39)
Completeness of resection
R0 64 (98.5)
R1 1 (1.5)
Total operative time (min) 614 (562, 673)
30-day readmission 13 (20.6)
Length of stay (days) 8 (7, 13.5)
In-hospital mortality 2 (3.1)
30-day mortality 2 (3.1)
90-day mortality 2 (3.1)
Table 3. Major morbidity
Variable N (%)
Pneumonia 9 (17)
Atrial arrhythmia requiring treatment 19 (38.8)
Anastomotic leak (grade ≥ 3) 3 (4.6)
Chylothorax requiring treatment 4 (8.3)
Recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis 0 (0)
Intraoperative complications 6 (9.2)
major morbidities, including pneumonia (P = 0.34), atrial arrhythmia requiring treatment (P = 0.19), and
anastomotic leaks graded ≥ 3 (P = 0.49).
DISCUSSION
This manuscript describes our current RAMIE technique at UPMC. The data suggest that RAMIE can be
performed with favorable outcomes at experienced institutions . These outcomes are comparable to those
[5]
reported in previous studies of MIE, particularly in terms of mortality rates, adequacy of oncologic
resection, and perioperative complications . This suggests that both patient and oncologic outcomes are
[5]
not compromised by the robotic approach.
RAMIE may be superior to MIE in the median number of lymph nodes harvested - 32 vs. 21 . This
[4,5]
difference likely reflects one of the key benefits of robotic surgery - enhanced surgical control and ease of
tissue dissection in anatomically challenging regions. Robotic technology provides surgeons with improved
[8]
visualization and greater dexterity for complex maneuvers . Harvesting a larger number of lymph nodes
may improve long-term oncologic outcomes by enabling more accurate pathological staging. While these
findings are encouraging, further studies are needed to determine whether the number of harvested lymph
nodes correlates with recurrence rates.
Two recent studies from our institution involving 25 and 65 patients, respectively, demonstrated a reduction
in median operative time from 661 to 614 min . This suggests that procedural efficiency improves with
[5,7]
increased surgeon and institutional experience. However, it remains unclear whether our results at a high-
volume center can be replicated in lower-volume institutions treating fewer patients with resectable
esophageal cancer. Given the complexity of this operation, having well-trained surgeons and staff is critical