Page 22 - Read Online
P. 22
Hashida et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2024;8:14 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2023.139 Page 5 of 8
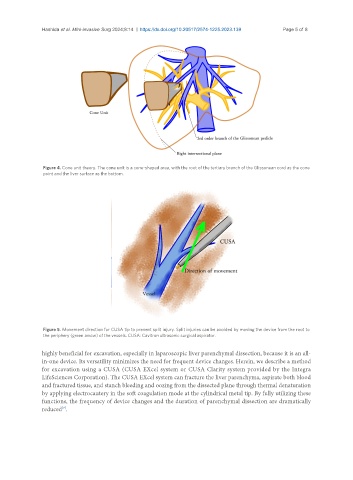
Figure 4. Cone unit theory. The cone unit is a cone-shaped area, with the root of the tertiary branch of the Glissonean cord as the cone
point and the liver surface as the bottom.
Figure 5. Movement direction for CUSA tip to prevent split injury. Split injuries can be avoided by moving the device from the root to
the periphery (green arrow) of the vessels. CUSA: Cavitron ultrasonic surgical aspirator.
highly beneficial for excavation, especially in laparoscopic liver parenchymal dissection, because it is an all-
in-one device. Its versatility minimizes the need for frequent device changes. Herein, we describe a method
for excavation using a CUSA (CUSA EXcel system or CUSA Clarity system provided by the Integra
LifeSciences Corporation). The CUSA EXcel system can fracture the liver parenchyma, aspirate both blood
and fractured tissue, and stanch bleeding and oozing from the dissected plane through thermal denaturation
by applying electrocautery in the soft coagulation mode at the cylindrical metal tip. By fully utilizing these
functions, the frequency of device changes and the duration of parenchymal dissection are dramatically
reduced .
[7]