Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
Page 299 Berber et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2021;5:292-303 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2021.35
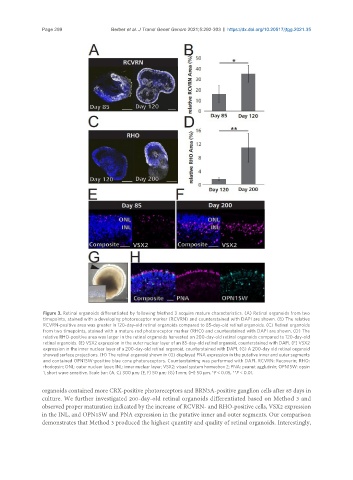
Figure 3. Retinal organoids differentiated by following Method 3 acquire mature characteristics. (A) Retinal organoids from two
timepoints, stained with a developing photoreceptor marker (RCVRN) and counterstained with DAPI are shown. (B) The relative
RCVRN-positive area was greater in 120-day-old retinal organoids compared to 85-day-old retinal organoids. (C) Retinal organoids
from two timepoints, stained with a mature rod photoreceptor marker (RHO) and counterstained with DAPI are shown. (D) The
relative RHO-positive area was larger in the retinal organoids harvested on 200-day-old retinal organoids compared to 120-day-old
retinal organoids. (E) VSX2 expression in the outer nuclear layer of an 85-day-old retinal organoid, counterstained with DAPI. (F) VSX2
expression in the inner nuclear layer of a 200-day-old retinal organoid, counterstained with DAPI. (G) A 200-day old retinal organoid
showed surface projections. (H) The retinal organoid shown in (G) displayed PNA expression in the putative inner and outer segments
and contained OPN1SW-positive blue cone photoreceptors. Counterstaining was performed with DAPI. RCVRN: Recoverin; RHO:
rhodopsin; ONL: outer nuclear layer; INL: inner nuclear layer; VSX2: visual system homeobox 2; PNA: peanut agglutinin; OPN1SW: opsin
1, short wave sensitive. Scale bar: (A, C) 300 µm; (E, F) 50 µm; (G) 1 mm; (H) 50 µm. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
organoids contained more CRX-positive photoreceptors and BRN3A-positive ganglion cells after 85 days in
culture. We further investigated 200-day-old retinal organoids differentiated based on Method 3 and
observed proper maturation indicated by the increase of RCVRN- and RHO-positive cells, VSX2 expression
in the INL, and OPN1SW and PNA expression in the putative inner and outer segments. Our comparison
demonstrates that Method 3 produced the highest quantity and quality of retinal organoids. Interestingly,