Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
Donskov et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2021;5:136-62 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2021.12 Page 13
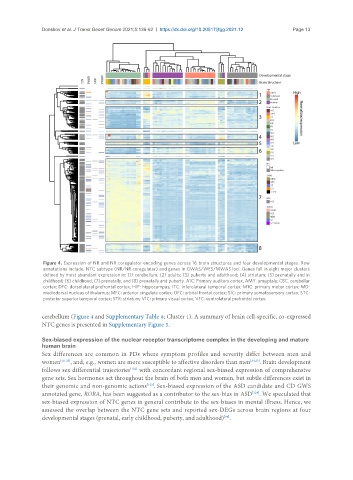
Figure 4. Expression of NR and NR coregulator encoding genes across 16 brain structures and four developmental stages. Row
annotations include: NTC subtype (NR/NR coregulator) and genes in GWAS/WES/MWAS loci. Genes fall in eight major clusters
defined by most abundant expression in: (1) cerebellum; (2) adults; (3) puberty and adulthood; (4) striatum; (5) prenatally and in
childhood; (6) childhood; (7) prenatally; and (8) prenatally and puberty. A1C: Primary auditory cortex; AMY: amygdala; CBC: cerebellar
cortex; DFC: dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; HIP: hippocampus; ITC: inferolateral temporal cortex; M1C: primary motor cortex; MD:
mediodorsal nucleus of thalamus; MFC: anterior cingulate cortex; OFC: orbital frontal cortex; S1C: primary somatosensory cortex; STC:
posterior superior temporal cortex; STR: striatum; V1C: primary visual cortex; VFC: ventrolateral prefrontal cortex.
cerebellum (Figure 4 and Supplementary Table 8; Cluster 1). A summary of brain cell-specific, co-expressed
NTC genes is presented in Supplementary Figure 5.
Sex-biased expression of the nuclear receptor transcriptome complex in the developing and mature
human brain
Sex differences are common in PDs where symptom profiles and severity differ between men and
women [20-25] , and, e.g., women are more susceptible to affective disorders than men [24,25] . Brain development
follows sex differential trajectories with concordant regional sex-biased expression of comprehensive
[122]
gene sets. Sex hormones act throughout the brain of both men and women, but subtle differences exist in
their genomic and non-genomic actions . Sex-biased expression of the ASD candidate and CD GWS
[123]
annotated gene, RORA, has been suggested as a contributor to the sex-bias in ASD . We speculated that
[124]
sex-biased expression of NTC genes in general contribute to the sex-biases in mental illness. Hence, we
assessed the overlap between the NTC gene sets and reported sex-DEGs across brain regions at four
[96]
developmental stages (prenatal, early childhood, puberty, and adulthood) .