Page 37 - Read Online
P. 37
Page 322 Genvigir et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:320-55 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.37
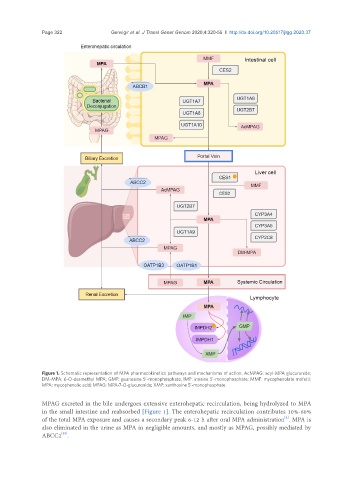
Figure 1. Schematic representation of MPA pharmacokinetics pathways and mechanisms of action. AcMPAG: acyl-MPA glucuronide;
DM-MPA: 6-O-desmethyl MPA; GMP: guanosine 5’-monophosphate; IMP: inosine 5’-monophosphate; MMF: mycophenolate mofetil;
MPA: mycophenolic acid; MPAG: MPA-7-O-glucuronide; XMP: xanthosine 5’-monophosphate
MPAG excreted in the bile undergoes extensive enterohepatic recirculation, being hydrolyzed to MPA
in the small intestine and reabsorbed [Figure 1]. The enterohepatic recirculation contributes 10%-60%
[1]
of the total MPA exposure and causes a secondary peak 6-12 h after oral MPA administration . MPA is
also eliminated in the urine as MPA in negligible amounts, and mostly as MPAG, possibly mediated by
[19]
ABCC2 .