Page 55 - Read Online
P. 55
Webb et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:71-80 I https://doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.11 Page 73
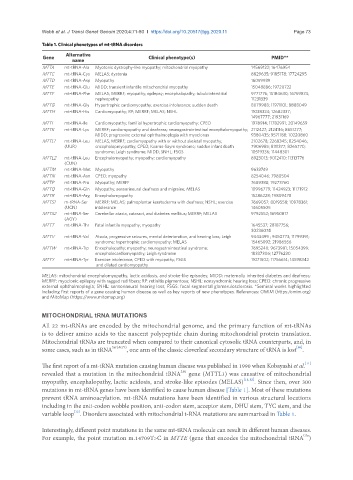
Table 1. Clinical phenotypes of mt-tRNA disorders
Alternative
Gene name Clinical phenotype(s) PMID**
MTTA mt-tRNA-Ala Myotonic dystrophy-like myopathy; mitochondrial myopathy 14569122; 16476954
MTTC mt-tRNA-Cys MELAS; dystonia 8829635; 9185178; 17724295
MTTD mt-tRNA-Asp Myopathy 16059939
MTTE mt-tRNA-Glu MIDD; transient infantile mitochondrial myopathy 15048886; 19720722
MTTF mt-tRNA-Phe MELAS; MERRF; myopathy; epilepsy; encephalopathy; tubulointerstitial 9771776; 15184630; 16769874;
nephropathy 11231339
MTTG mt-tRNA-Gly Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; exercise intolerance; sudden death 8079988; 11971101; 8888049
MTTH mt-tRNA-His Cardiomyopathy; RP; MERRF; MELAS; NSHL 11038324; 12682337;
14967777; 21931169
MTTI mt-tRNA-Ile Cardiomyopathy; familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; CPEO 1978914; 11782991; 20149659
MTTK mt-tRNA-Lys MERRF; cardiomyopathy and deafness; neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy; 2112427; 2124116; 8651277;
MIDD; progressive external ophthalmoplegia with myoclonus 9380435; 9571188; 10220860
MTTL1 mt-tRNA-Leu MELAS; MERRF; cardiomyopathy with or without skeletal myopathy; 2102678; 2268345; 8254046;
(UUR) encephalopmyopathy; CPEO; Kearns-Sayre syndrome; sudden infant death 7906985; 8111377; 8265770;
syndrome; Leigh syndrome; MIDD; SNHL; FSGS 10519336; 11448301
MTTL2 mt-tRNA-Leu Encephalomyopathy; myopathy; cardiomyopathy 8923013; 9012410; 11313776
(CUN)
MTTM mt-tRNA-Met Myopathy 9633749
MTTN mt-tRNA-Asn CPEO; myopathy 8254046; 7980504
MTTP mt-tRNA-Pro Myopathy; MERFF 7689388; 19273760
MTTQ mt-tRNA-Gln Myopathy; sensorineural deafness and migraine; MELAS 10996779; 11424923; 11171912
MTTR mt-tRNA-Arg Encephalomyopathy 15286228; 19809478
MTTS1 m-tRNA-Ser MERRF; MELAS; palmoplantar keratoderma with deafness; NSHL; exercise 7669057; 8019558; 10978361;
(UCN) intolerance 14605505
MTTS2 mt-tRNA-Ser Cerebellar ataxia, cataract, and diabetes mellitus; MERRF; MELAS 9792552; 16950817
(AGY)
MTTT mt-tRNA-Thr Fatal infantile myopathy; myopathy 1645537; 28187756;
30236074
MTTV mt-tRNA-Val Ataxia, progressive seizures, mental deterioration, and hearing loss; Leigh 9443499 ; 9450773; 11799391;
syndrome; hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; MELAS 15465092; 21986556
MTTW mt-tRNA-Trp Encephalopathy; myopathy; neurogastrointestinal syndrome; 7695240; 9673981; 15054399;
encephalocardiomyopathy; Leigh syndrome 18337306; 12776230
MTTY mt-tRNA-Tyr Exercise intolerance; CPEO with myopathy; FSGS 11071502; 11756614; 14598342
and dilated cardiomyopathy
MELAS: mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes; MIDD: maternally inherited diabetes and deafness;
MERRF: myoclonic epilepsy with ragged red fibers; RP: retinitis pigmentosa; NSHL: nonsyndromic hearing loss; CPEO: chronic progressive
external ophthalmoplegia; SNHL: sensorineural hearing loss; FSGS: focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. *Seminal works highlighted
including first reports of a gene causing human disease as well as key reports of new phenotypes. References: OMIM (https:/omim.org)
and MitoMap (https://www.mitomap.org)
MITOCHONDRIAL tRNA MUTATIONS
All 22 mt-tRNAs are encoded by the mitochondrial genome, and the primary function of mt-tRNAs
is to deliver amino acids to the nascent polypeptide chain during mitochondrial protein translation.
Mitochondrial tRNAs are truncated when compared to their canonical cytosolic tRNA counterparts, and, in
[10]
some cases, such as in tRNA Ser(AGY) , one arm of the classic cloverleaf secondary structure of tRNA is lost .
[11]
The first report of a mt-tRNA mutation causing human disease was published in 1990 when Kobayashi et al.
Leu
revealed that a mutation in the mitochondrial tRNA gene (MTTL1) was causative of mitochondrial
myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) [11,12] . Since then, over 300
mutations in mt-tRNA genes have been identified to cause human disease [Table 1]. Most of these mutations
prevent tRNA aminoacylation. mt-tRNA mutations have been identified in various structural locations
including in the anti-codon wobble position, anti-codon stem, acceptor stem, DHU stem, TYC stem, and the
[12]
variable loop . Disorders associated with mitochondrial t-RNA mutations are summarized in Table 1.
Interestingly, different point mutations in the same mt-tRNA molecule can result in different human diseases.
For example, the point mutation m.14709T>C in MTTE (gene that encodes the mitochondrial tRNA )
Glu