Page 57 - Read Online
P. 57
Webb et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:71-80 I https://doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.11 Page 75
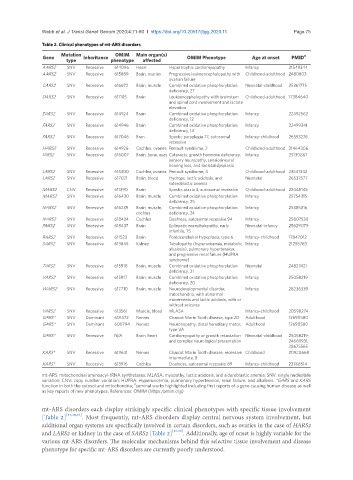
Table 2. Clinical phenotypes of mt-ARS disorders
Mutation OMIM Main organ(s) #
Gene type Inheritance phenotype affected OMIM Phenotype Age at onset PMID
AARS2 SNV Recessive 614096 Heart Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Infancy 21549344
AARS2 SNV Recessive 615889 Brain, ovaries Progressive leukoencephalopathy with Childhood-adulthood 2480803
ovarian failure
CARS2 SNV Recessive 616672 Brain, muscle Combined oxidative phosphorylation Neonatal-childhood 25361775
deficiency, 27
DARS2 SNV Recessive 611105 Brain Leukoencephalopathy with brainstem Childhood-adulthood 17384640
and spinal cord involvement and lactate
elevation
EARS2 SNV Recessive 614924 Brain Combined oxidative phosphorylation Infancy 22492562
deficiency, 12
FARS2 SNV Recessive 614946 Brain Combined oxidative phosphorylation Infancy 22499341
deficiency, 14
FARS2 SNV Recessive 617046 Bran Spastic paraplegia 77, autosomal Infancy-childhood 26553276
recessive
HARS2 SNV Recessive 614926 Cochlea, ovaries Perrault syndrome, 2 Childhood-adulthood 21464306
IARS2 SNV Recessive 616007 Brain, bone, eyes Cataracts, growth hormone deficiency, Infancy 25130867
sensory neuropathy, sensiorineural
hearing loss, and skeletal dysplasia
LARS2 SNV Recessive 615300 Cochlea, ovaries Perrault syndrome, 4 Childhood-adulthood 23541342
LARS2 SNV Recessive 617021 Brain, blood Hydrops, lactic acidosis, and Neonatal 26537577
sideroblastic anemia
MARS2 CNV Recessive 611390 Brain Spastic ataxia 3, autosomal recessive Childhood-adulthood 22448145
MARS2 SNV Recessive 616430 Brain, muscle Combined oxidative phosphorylation Infancy 25754315
deficiency, 25
NARS2 SNV Recessive 616239 Brain, muscle, Combined oxidative phosphorylation Infancy 25385316
cochlea deficiency, 24
NARS2 SNV Recessive 618434 Cochlea Deafness, autosomal recessive 94 Infancy 25807530
PARS2 SNV Recessive 618437 Brain Epilepetic encephalopathy, early Neonatal-infancy 25629079
infantile, 75
RARS2 SNV Recessive 611523 Brain Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 6 Infancy-childhood 17847012
SARS2 SNV Recessive 613845 Kidney Tubulopathy (hyperuricemia, metabolic Infancy 21255763
alkalosis), pulmonary hypertension,
and progressive renal failure (HUPRA
syndrome)
TARS2 SNV Recessive 615918 Brain, muscle Combined oxidative phosphorylation Neonatal 24827421
deficiency, 21
VARS2 SNV Recessive 615917 Brain, muscle Combined oxidative phosphorylation Infancy 25058219
deficiency, 20
WARS2 SNV Recessive 617710 Brain, muscle Neurodevelopmental disorder, Infancy 28236339
mitochondria, with abnormal
movements and lactic acidosis, with or
without seizures
YARS2 SNV Recessive 613561 Muscle, blood MLASA Infancy-childhood 20598274
GARS* SNV Dominant 601472 Nerves Charcot Marie Tooth disease, type 2D Adulthood 12690580
GARS* SNV Dominant 600794 Nerves Neuronopathy, distal hereditary motor, Adulthood 12690580
type VA
GARS* SNV Recessive N/A Brain, heart Cardiomyopathy or growth retardation Neonatal-childhood 25058219;
and complex neurological presentation 24669931;
28675565
KARS* SNV Recessive 613641 Nerves Charcot Marie Tooth disease, recessive Childhood 20920668
intermediate, B
KARS* SNV Recessive 613916 Cochlea Deafness, autosomal recessive 89 Infancy-childhood 23768514
mt-ARS: mitochondrial aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases; MLASA: myopathy, lactic acidosis, and sideroblastic anemia; SNV: single nucleotide
variation; CNV: copy number variation; HUPRA: Hyperuricemia, pulmonary hypertension, renal failure, and alkalosis. *GARS and KARS
function in both the cytosol and mitochondria; seminal works highlighted including first reports of a gene causing human disease as well
#
as key reports of new phenotypes. References: OMIM (https:/omim.org)
mt-ARS disorders each display strikingly specific clinical phenotypes with specific tissue involvement
[Table 2] [17,20,21] . Most frequently, mt-ARS disorders display central nervous system involvement, but
additional organ systems are specifically involved in certain disorders, such as ovaries in the case of HARS2
and LARS2 or kidney in the case of SARS2 [Table 2] [22-24] . Additionally, age of onset is highly variable for the
various mt-ARS disorders. The molecular mechanisms behind this selective tissue involvement and disease
phenotype for specific mt-ARS disorders are currently poorly understood.