Page 59 - Read Online
P. 59
Webb et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:71-80 I https://doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.11 Page 77
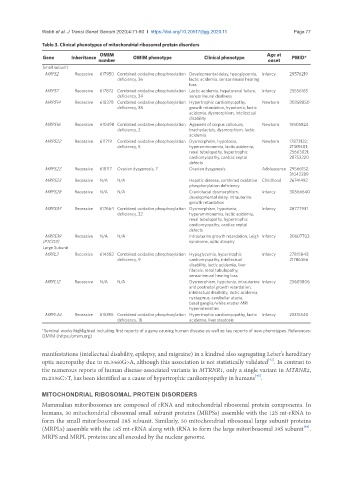
Table 3. Clinical phenotypes of mitochondrial ribosomal protein disorders
OMIM Age at
Gene Inheritance number OMIM phenotype Clinical phenotype onset PMID*
Small subunit
MRPS2 Recessive 617950 Combined oxidative phosphorylation Developmental delay, hypoglycemia, Infancy 29576219
deficiency, 36 lactic acidemia, sensorineural hearing
loss
MRPS7 Recessive 617872 Combined oxidative phosphorylation Lactic acidemia, hepatorenal failure, Infancy 25556185
deficiency, 34 sensorineural deafness
MRPS14 Recessive 618378 Combined oxidative phosphorylation Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Newborn 30358850
deficiency, 38 growth retardation, hypotonia, lactic
acidemia, dysmorphism, intellectual
disability
MRPS16 Recessive 610498 Combined oxidative phosphorylation Agenesis of corpus callosum, Newborn 15505824
deficiency, 2 brachydactyly, dysmorphism, lactic
acidemia
MRPS22 Recessive 611719 Combined oxidative phosphorylation Dysmorphism, hypotonia, Newborn 17873122;
deficiency, 5 hyperammonemia, lactic acidemia, 21189481;
renal tubulopathy, hypertrophic 25663021;
cardiomyopathy, cardiac septal 28752220
defects
MRPS22 Recessive 618117 Ovarian dysgenesis, 7 Ovarian dysgenesis Adolescence 29566152;
31042289
MRPS23 Recessive N/A N/A Hepatic disease, combined oxidative Childhood 26741492
phosphorylation deficiency
MRPS28 Recessive N/A N/A Craniofacial dysmorphism, Infancy 30566640
developmental delay, intrauterine
growth retardation
MRPS34 Recessive 617664 Combined oxidative phosphorylation Dysmorphism, hypotonia, Infancy 28777931
deficiency, 32 hyperammonemia, lactic acidemia,
renal tubulopathy, hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy, cardiac septal
defects
MRPS39 Recessive N/A N/A Intrauterine growth retardation, Leigh Infancy 30607703
(PTCD3) syndrome, optic atrophy
Large Subunit
MRPL3 Recessive 614582 Combined oxidative phosphorylation Hypoglycemia, hypertrophic Infancy 27815843;
deficiency, 9 cardiomyopathy, intellectual 21786366
disability, lactic acidemia, liver
fibrosis, renal tubulopathy,
sensorineural hearing loss
MRPL12 Recessive N/A N/A Dysmorphism, hypotonia, intrauterine Infancy 23603806
and postnatal growth retardation,
intellectual disability, lactic acidemia,
nystagmus, cerebellar ataxia,
basal ganglia/white matter MRI
hyperintensities
MRPL44 Recessive 615395 Combined oxidative phosphorylation Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, lactic Infancy 23315540
deficiency, 16 acidemia, liver steatosis
*Seminal works highlighted including first reports of a gene causing human disease as well as key reports of new phenotypes. References:
OMIM (https:/omim.org)
manifestations (intellectual disability, epilepsy, and migraine) in a kindred also segregating Leber’s hereditary
[42]
optic neuropathy due to m.3460G>A, although this association is not statistically validated . In contrast to
the numerous reports of human disease-associated variants in MTRNR1, only a single variant in MTRNR2,
[43]
m.2336C>T, has been identified as a cause of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in humans .
MITOCHONDRIAL RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN DISORDERS
Mammalian mitoribosomes are composed of rRNA and mitochondrial ribosomal protein components. In
humans, 30 mitochondrial ribosomal small subunit proteins (MRPSs) assemble with the 12S mt-rRNA to
form the small mitoribosomal 28S subunit. Similarly, 50 mitochondrial ribosomal large subunit proteins
[44]
(MRPLs) assemble with the 16S mt-rRNA along with tRNA to form the large mitoribosomal 39S subunit .
MRPS and MRPL proteins are all encoded by the nuclear genome.